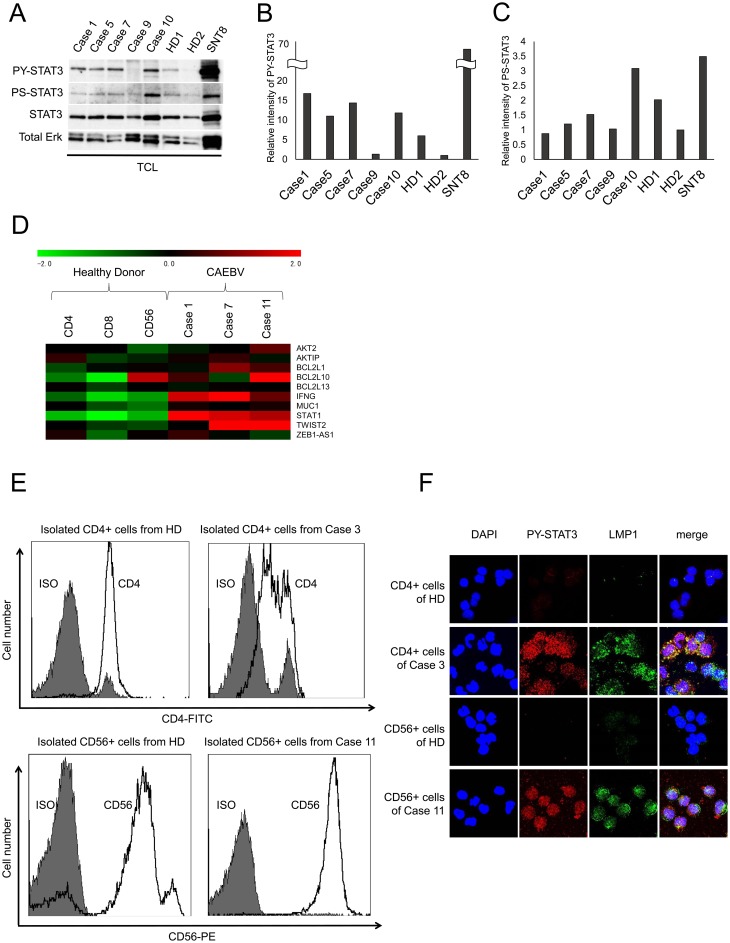
Figure 2. STAT3 is constitutively activated in patient-derived EBV-infected T or NK cells.
(A) Western blotting for the phosphorylation of the PBMCs obtained from patients with CAEBV. Total cell lysates (TCL) were prepared, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted with antibodies, as indicated. STAT3 is constitutively phosphorylated in the PBMCs from patients with CAEBV, except for Case 9. The phosphorylation was relatively weak or not detected in cells from healthy donors (HD). SNT8 is a positive control. (B and C); the relative intensities of tyrosine-phosphorylated STAT3 (PY-STAT3) (B) and serine-phosphorylated STAT3 (PS-STAT3) (C) bands of (A) were determined as ratio to total STAT3 by densitometry. HD 2 was determined as a control. (D) the expression of STAT3 responsible genes in the T- or NK-cell fractions of the PBMCs containing EBV-infected cells from CAEBV patients. The EBV-infected cell fractions were CD4-, CD8-, and CD56-positive cells from Cases 1, 7, and 11, respectively. The same cell fractions from HD were examined as EBV-negative controls. A heat map shows the expression levels from genes induced by STAT3 in the patient-derived PBMCs fractions containing EBV-infected cells and control samples. (E and F) STAT3 activation in EBV-positive and CD4- or CD56-positive cells from patients with CAEBV. CD4- and CD56-positive cells were isolated using anti-CD4 and anti-CD56 antibody-conjugated magnetic beads from the peripheral blood of Cases 3, 11, respectively. The same cell fractions from HD were examined as EBV-negative controls. (E) surface CD4 and CD56 expression is confirmed by flow cytometry using antibodies to CD4 and CD56 (open histogram). The gray, shaded histograms are isotype-matched control immunoglobulin. Top, Case 3; bottom, Case 11. (F) the tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 in isolated cells is demonstrated by immunofluorescence staining. Nuclear as well as cytoplasmic localization of STAT3 is detected in patients but not in HDs.