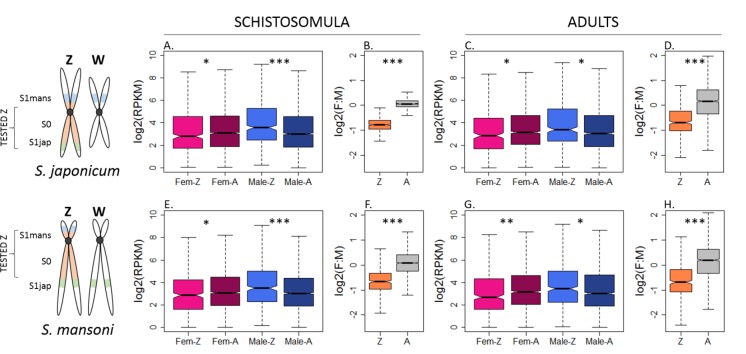
Figure 2. Patterns of expression on the Z and autosomes of S.japonicum and S. mansoni.
Z-linked and autosomal gene expression patterns are shown for S. japonicum (A-D) and S. mansoni (E-H), in undifferentiated schistosomula and sexually mature adults. In panels A, C, E, and G, Fem-Z and Male-Z refer to the expression of Z-linked genes in females and males, respectively, and Fem-A and Male-A to the expression of the autosomal genes in females and males. In panels B, D, F, and H, Z refers to Z-linked genes and A to autosomal genes. In all conditions, a strong male bias is observed for the Z-linked genes (B, D, F, H). This male-biased expression of the Z-linked genes is accompanied by both an under-expression in females and an over-expression in males, compared to the level of autosomal expression (A, C, E, G). The level of significance of each comparison (Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction) is indicated by asterisks: *p-value<0.05, **p-value<0.001, ***p-value<0.0001.
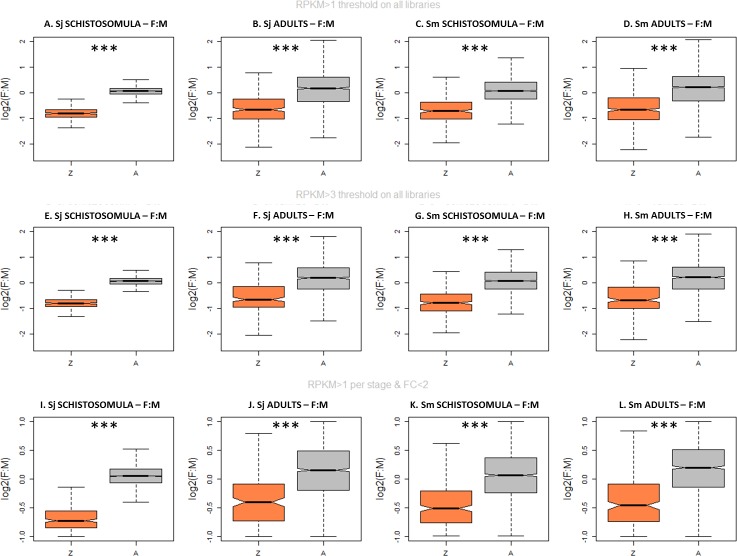
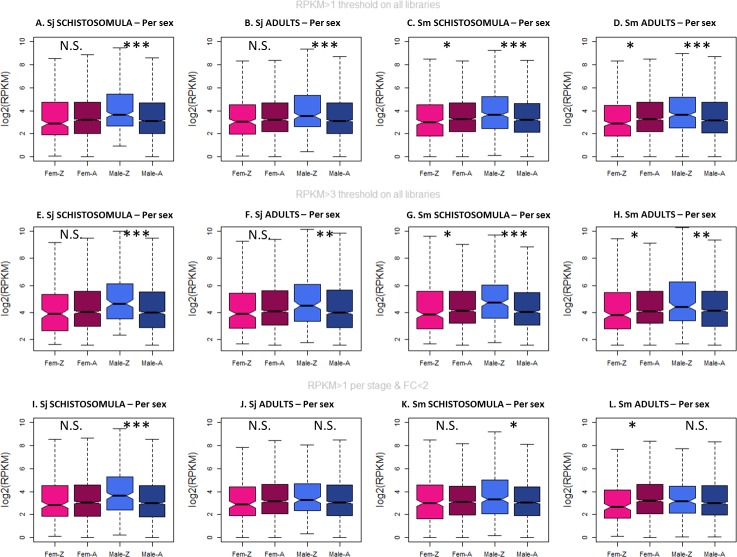
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Adult expression patterns (RPKM>1, exhaustive strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.

Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Adult expression patterns (RPKM>0, exhaustive strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.

Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Adult expression patterns (RPKM>1, stringent strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.
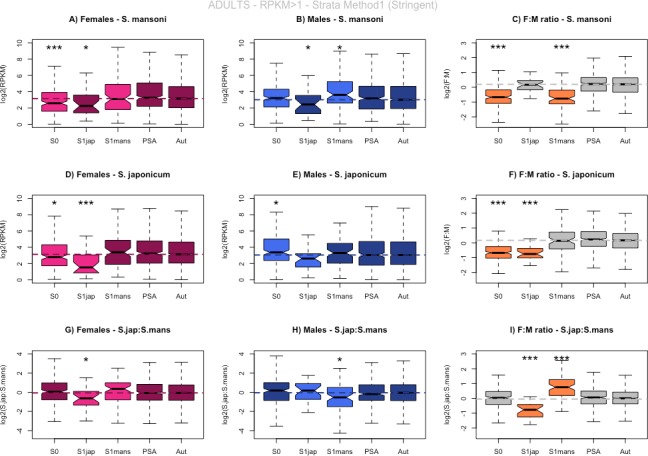
Figure 2—figure supplement 4. Adult expression patterns (RPKM>0, stringent strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.
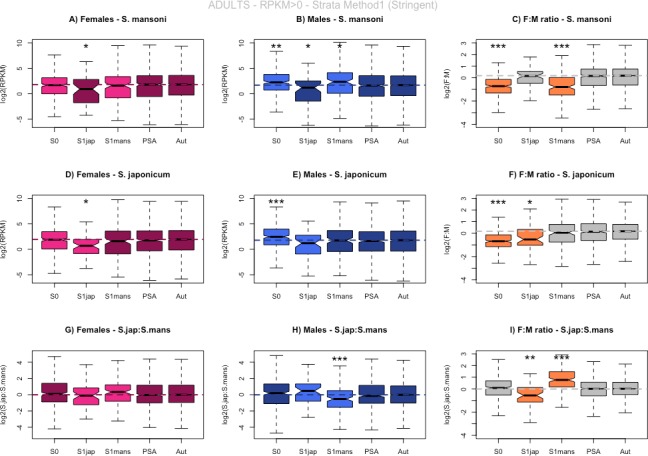
Figure 2—figure supplement 5. Adult expression patterns (RPKM>1, exhaustive strata, Wormbase orthologs) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.

Figure 2—figure supplement 6. Adult expression patterns (TPM>1, exhaustive strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.

Figure 2—figure supplement 7. Adult expression patterns (TPM>0, exhaustive strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.
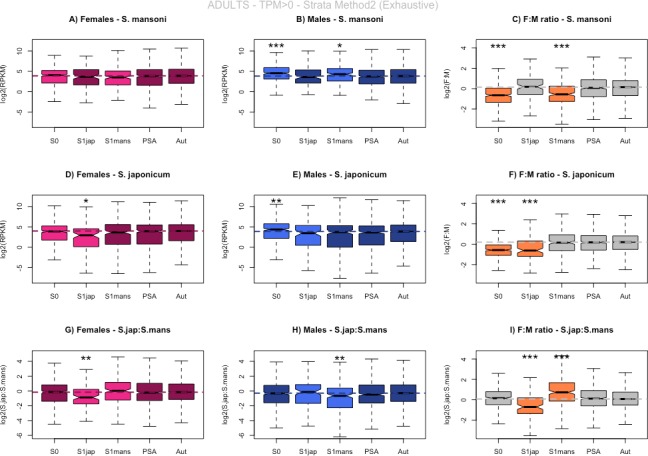
Figure 2—figure supplement 8. Schistosomula expression patterns (RPKM>1, exhaustive strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.
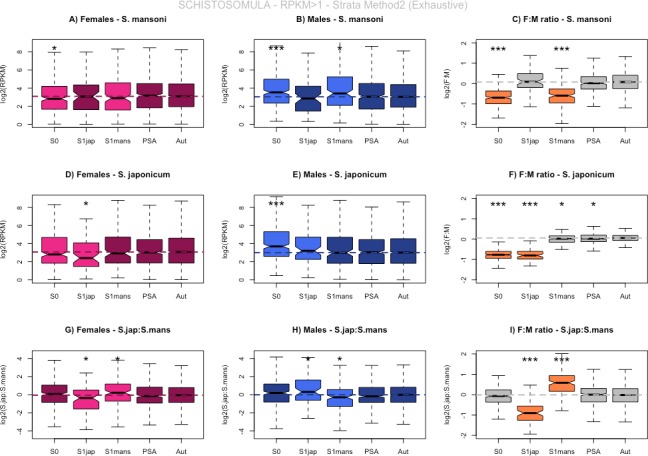
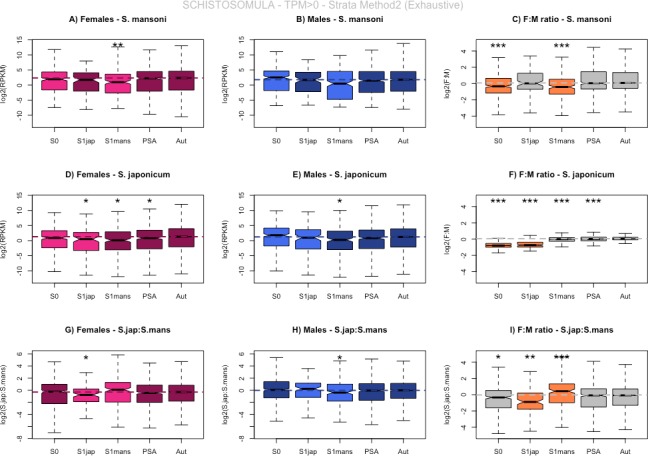
Figure 2—figure supplement 9. Schistosomula expression patterns (RPKM>0, exhaustive strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.

Figure 2—figure supplement 10. Schistosomula expression patterns (RPKM>1, stringent strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.

Figure 2—figure supplement 11. Schistosomula expression patterns (RPKM>0, stringent strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.

Figure 2—figure supplement 12. Schistosomula expression patterns (RPKM>1, exhaustive strata, Wormbase orthologs) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.

Figure 2—figure supplement 13. Schistosomula expression patterns (TPM>1, exhaustive strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.
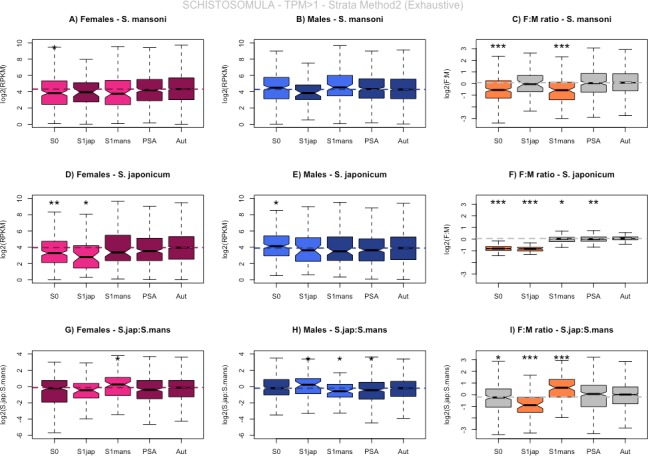
Figure 2—figure supplement 14. Schistosomula expression patterns (TPM>0, exhaustive strata) of genes located in the different strata of the Z (S0, S1man and S1jap), as well as pseudoautosomal and autosomal genes.