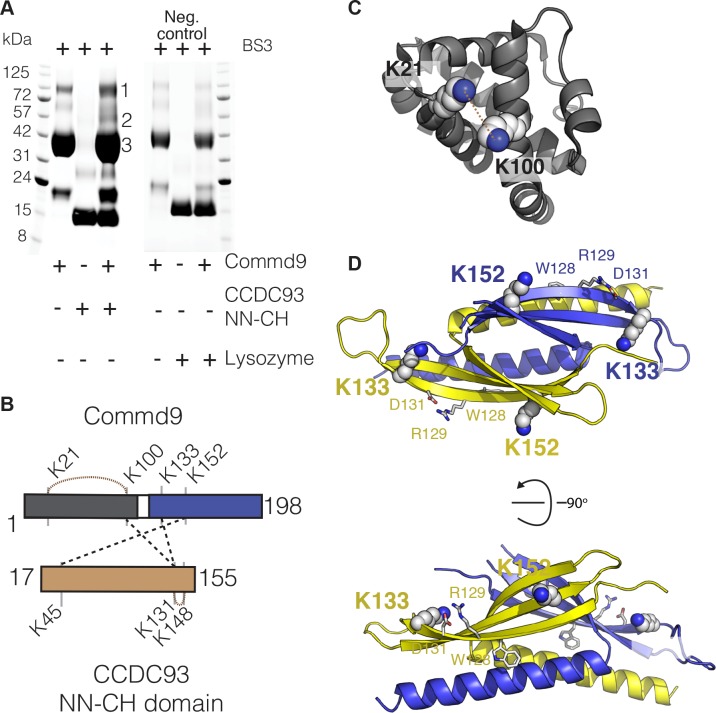
Figure 7. COMMD proteins bind to NN-CH domain of CCDC93 via the conserved WRVD motif in the COMM domain.
(A) Cross-linking of Commd9, NN-CH domain of CCDC93 and the mixture of two with BS3 for 30 min at room temperature. Three distinguishable SDS-PAGE gel bands were excised in the complex mixture sample (indicated by the number 1, 2 and 3) for MS analysis. In parallel, a cross-linking reaction between Commd9 and lysozyme was performed under the same condition. (B) Cross-link map for Commd9 in complex with the NN-CH domain of CCDC93. Intermolecular and intramolecular cross-linked peptides are labelled as black and brown dot lines respectively. (C and D) Ribbon representation of the Commd9 HN (C) and (D) COMM domain structures with mapped intramolecular and intermolecular cross-linked lysine residues (in spheres). In the Commd9 COMM domain, K133 and K152 are part of a contiguous surface that includes the side-chains of the conserved residues 128WRVD131 (indicated with sticks).