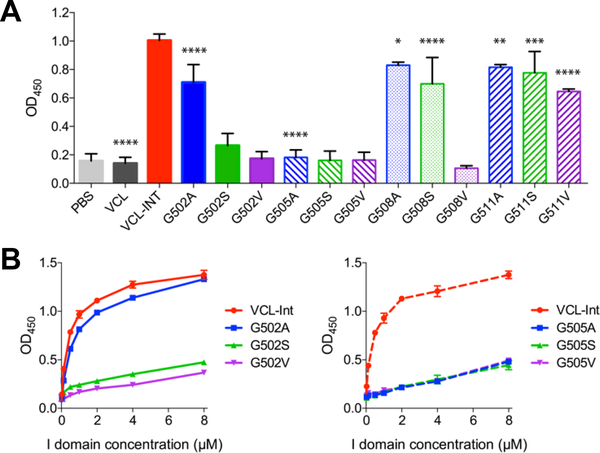
Figure 5.
Solid-state binding assay of integrin α2 I domain binding to all recombinant bacterial collagens. A. VCL-Int and all Gly substitution constructs were immobilized on 96-well microplates and incubated with 20 μg/ml (0.4 μM) of I domain. Bound proteins were detected with anti-GST HRP antibodies and measured as absorbance at 450 mn. Experiments were carried out in triplicates, with results based on the averages of data points and standard deviations presented as error bars. The significance level was determined by p value using paired Student’s t test between the means of VCL-Int and other samples. Statistically significant levels were marked with asterisks: *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001. B. Dose response of I domain to recombinant collagens with Gly substitution at Gly-502 and Gly- 505 positions adsorbed onto 96-well microplates. To cover all samples on the same 96-well microplate, the experiments for the dose-response curves consisted of duplicate or triplicate measurements and two independent dose response curves of I domain to VCL-Int were performed.