Figure 4. Interactions between LTi cell and T or B cells in the adaptive immune system.
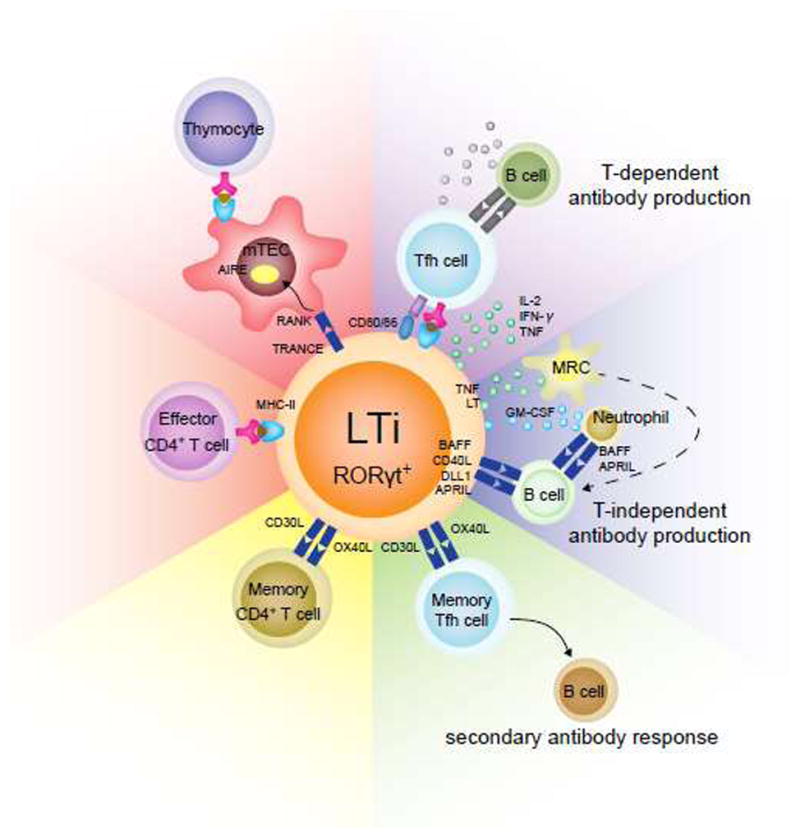
LTi cells can affect development and functions of T and B cells in the adaptive immune system through multiple mechanisms. They interact with the mTECs through RNAK/TRANCE interaction and thus induce the expression of AIRE, which is critical for T cell central tolerance. LTi cells can also directly regulate the effector T cell responses through antigen presentation by MHC-II. The adult LTi-like cells specifically express OX40L and CD30L, which may promote the survival of memory CD4+ T cells. The same mechanism may be responsible for the survival of memory follicular T helper (Tfh) cells and maintenance of memory antibody responses. In addition, LTi cells may promote antibody production by B cells through both T-dependent and -independent manners. Antigen presentation and cytokine secretion to Tfh cells from LTi cells can enhance B cell responses. Alternatively, LTi cells may directly activate B cell through BAFF, CD40L, DLL1 and APRIL expression. TNF, lymphotoxin (LT), and GM-CSF expression by LTi can also activate B cells through marginal reticular cells (MRC) and neutrophils.
