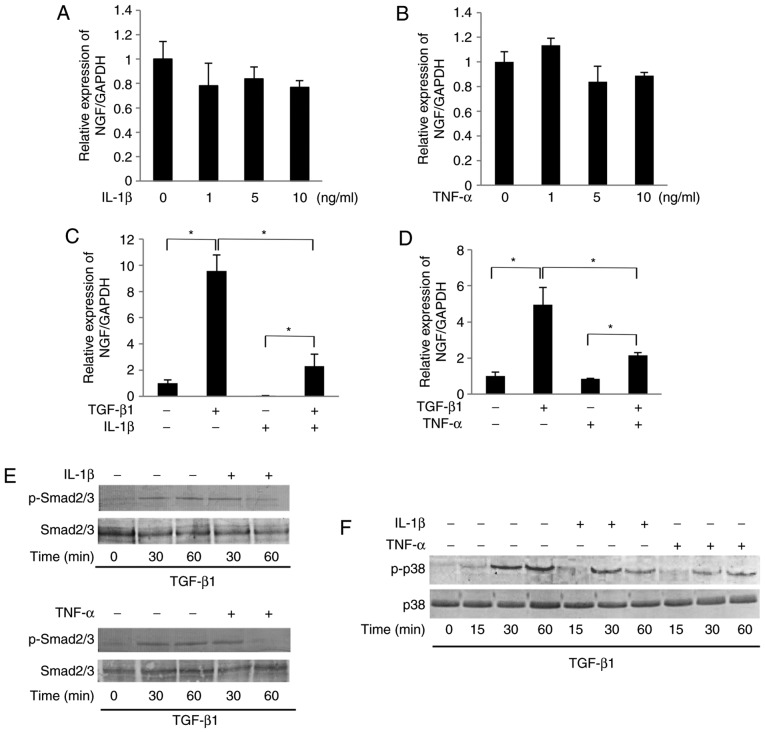
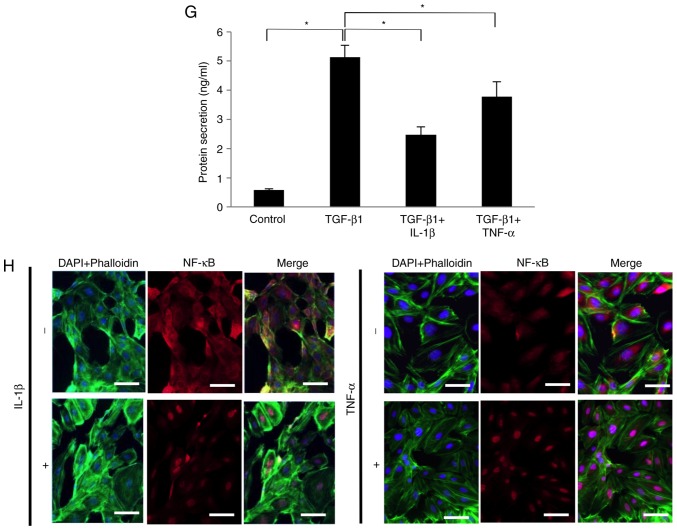
Figure 3.
IL-1β and TNF-α suppressed the TGF-β1-induced mRNA expression of NGF in SCDC2 cells by abrogating Smad2/3 and p38 MAPK activities. The effects of IL-1β and TNF-α on TGF-β1-induced mRNA expression of NGF in SCDC2 cells were evaluated using RT-qPCR. The cells were treated with or without (A) IL-1β alone or (B) TNF-α alone at indicated concentrations, (C) TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) and/or IL-1β (10 ng/ml), and (D) TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) and/or TNF-α (10 ng/ml). Data represent the mean ± standard deviation (n=6). *P<0.05. Phosphorylation status of (E) Smad2/3 and (F) p38 MAPK was evaluated using western blot analysis in cells treated with or without TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) alone, TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) + IL-1β (10 ng/ml), or TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) + TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for the indicated times. (G) NGF protein concentration secreted into the culture medium was determined using ELISA in cells cultured with or without TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) alone, TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) + IL-1β (10 ng/ml), or TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) + TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 5 days. (H) Nuclear translocation status of NF-κB p65 (red) was evaluated using immunofluorescence analysis (blue, nuclei; green, filamentous actin) in SCDC2 cells treated with or without IL-1β (10 ng/ml) or TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 24 h (×200 magnification; scale bar, 50 µm). IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TGF, transforming growth factor; NGF, nerve growth factor; SCDC, single cell-derived culture; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase.