Figure 1.
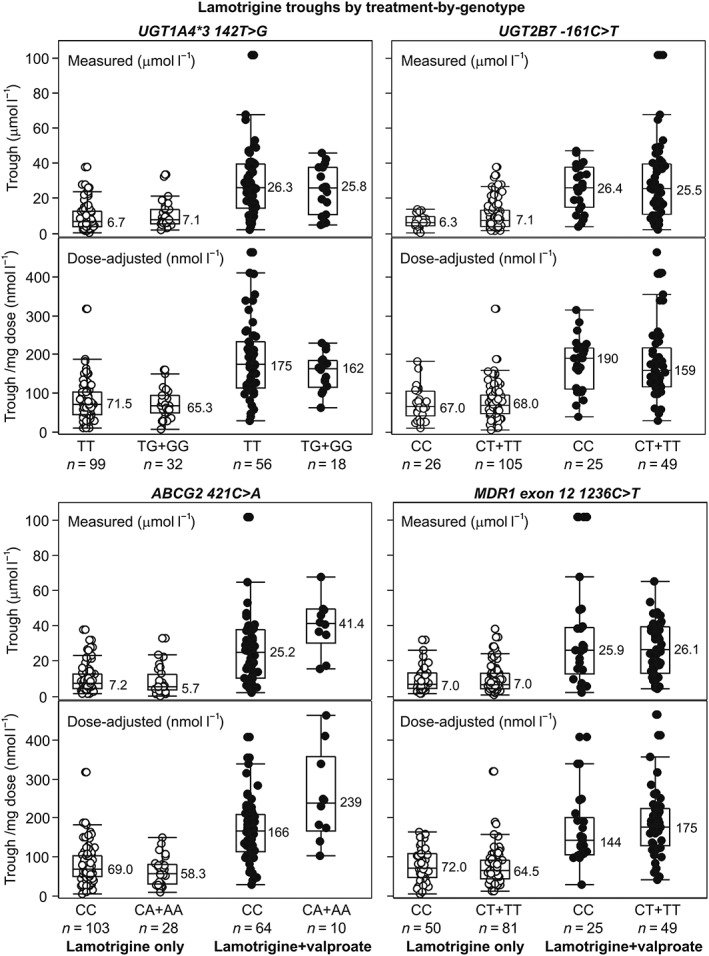
Measured and dose‐adjusted (per mg dose) steady‐state lamotrigine troughs by treatment‐by‐genotype – wild type homozygosity vs. variant allele carriage at UGT and ABC transporter loci, except for UGT1A4*2. Depicted are individual values (circles), medians (horizontal lines and numerical values), quartiles (boxes) and inner fences (bars). Values outside fences are outliers. For the lamotrigine‐treated wild type subjects at UGT1A4*2 (n = 128) measured lamotrigine troughs ranged between 0.5 and 37.6 μmol l–1 (median 6.6) and dose‐adjusted troughs ranged between 6.5 and 318 nmol l–1 (median 68.0). For the three variant allele carriers, the respective values were 5.2, 12.5 and 23.8 μmol l–1 (measured) and 79.3, 104.0 and 125 nmol l–1 (dose‐adjusted), i.e. within the wild type range. For the lamotrigine + valproate‐treated wild type subjects (n = 71), measured lamotrigine troughs ranged between 2.3 and 102 μmol l–1 (median 25.9) and dose‐adjusted troughs ranged between 30.7 and 464 nmol l–1 (median171.6). For the three variant allele carriers, the respective values were 6.5, 49.3 and 67.8 μmol l–1 (measured) and 130, 247 and 339 nmol l–1 (dose‐adjusted), i.e. within the wild type range. Data illustrate the valproate effect and do not indicate any effect of the variant allele carriage
