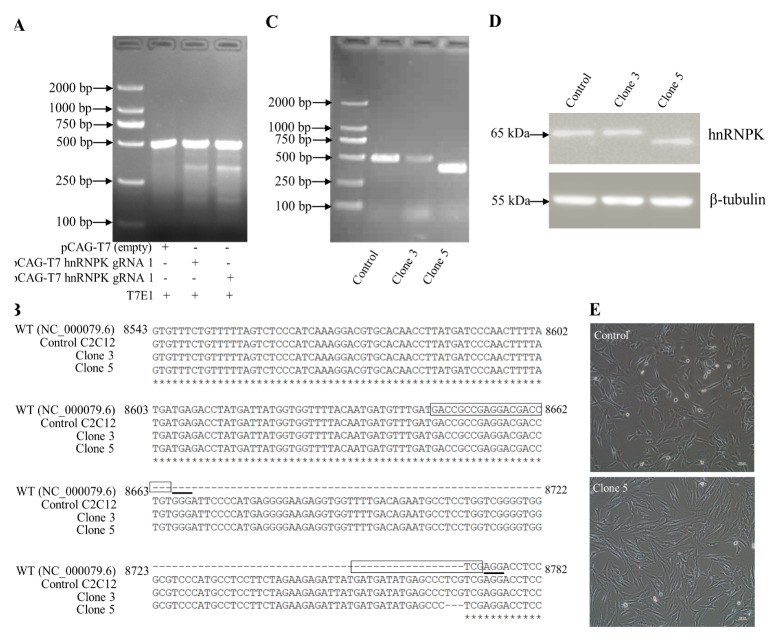
Fig. 2.
Generation and validation of hnRNPK-mutated cell lines. (A) Mismatch-specific endonuclease assay. Genomic PCR products spanning exon 12 of hnRNPK were amplified from the C2C12 cells transfected with pCAG-T7-Cas9-hnRNPK guide. (B) After clone isolation, gPCR amplicons encompassing the modified locus of genomic DNA were run on a 1.5% agarose gel. (C) Cell lysates of control and clonal hnRNPK mutated isolates, probed with specific hnRNPK antibodies. (D) Sequence alignment of bases 8543–8782 of exon 12 of the mouse hnRNPK sequence (NC_000079.6), a WT allele from control C2C12 cells, and two mutant alleles identified from each of the two hnRNPK-mutated clones. The complementary plus-strand sequences corresponding to the 20-nt target and 3-nt PAM are highlighted in a box and underlined, respectively. (E) The morphological changes of WT control and clone 5 cells. Scale bar = 100 μm.