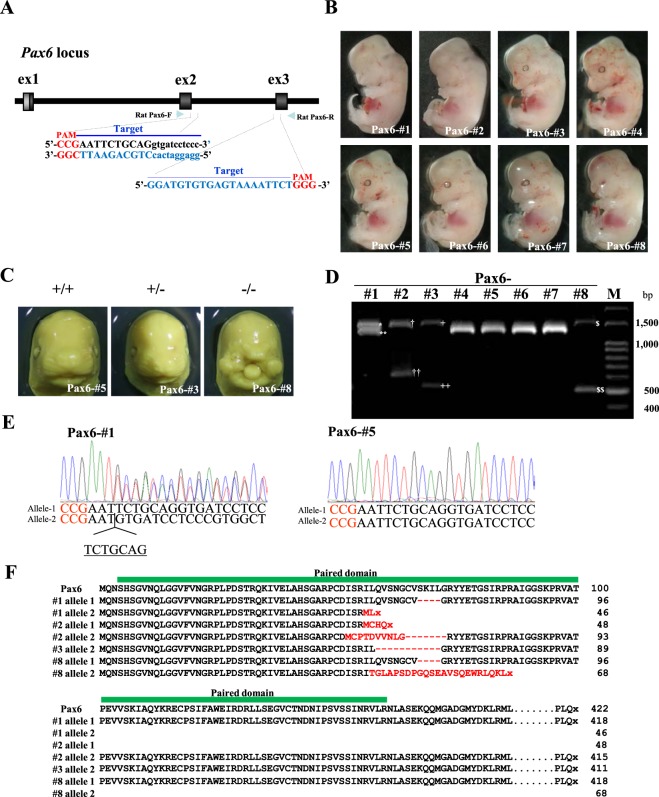
Figure 4.
(A) Schematic illustration of the wild-type Pax6 locus. Exons (ex1 to ex3) and introns are indicated by black boxes and a black line, respectively. Dual guide RNAs were used on the Pax6 locus: namely, the two target sequences recognized by gRNA are overlined and the PAM sequences are shown in red. The position of primers (Rat Pax6-F and -R) used to identify indels around the target sequences is indicated by arrowheads. (B) Fetal offspring (Pax6-#1 to #8) at 16.5 dpc obtained after i-GONAD targeted towards the paired domain of Pax6. Various abnormal phenotypes such as deformity of the facial structure together with loss of eye cup (as exemplified by Pax6-#1, #2 and #8) are discernible. (C) Representative 16.5 dpc fetuses exhibiting various types of craniofacial structure. Fetus Pax6-#5 and -#3 exhibited normal facial structure, and was wild-type and heterozygous for Pax6, respectively. Fetus Pax6-#8 completely lacked eyes and the lateral nasal prominence, and was homozygous knockout for Pax6. (D) Genotyping of the fetuses shown in (B). Fetuses Pax6-#1 to #3 and #8 have heterozygous PCR products (*allele-1of Pax6-#1, **allele-2 of Pax6-#1, †allele-1of Pax6-#2, ††allele-2 of Pax6-#2, +allele-1of Pax6-#3, ++allele-2 of Pax6-#3, $allele-1of Pax6-#8 and $$allele-2 of Pax6-#8). Fetuses Pax6-#4 to #7 have wild-type PCR products (1,489 bp). (E) Direct sequencing of PCR products derived from the animals shown in (B). Fetus Pax6-#5, which was judged as wild-type through morphological inspection (shown in B and C) and genotyping (shown in D), exhibited normal sequence for Pax6. In contrast, fetus Pax6-#1, which was judged as KO through morphological inspection (shown in B) and genotyping (shown in D), exhibited a 7 bp sequence deletion (underlined) in front of the PAM (shown in red). (F) Comparison of PAX6 amino acid sequences from fetuses derived from SD females subjected to i-GONAD-mediated induction of indels at the Pax6 locus. The control amino acid sequence of wild-type PAX6 protein is shown on the top. The amino acid sequences of the mutated PAX6 proteins (derived from Pax6-#1 to #3 and #8) are shown. Predicted consequences of the mutation on amino acid sequences are highlighted in red. Stop codons are shown as x. The green bar indicates the paired domain.