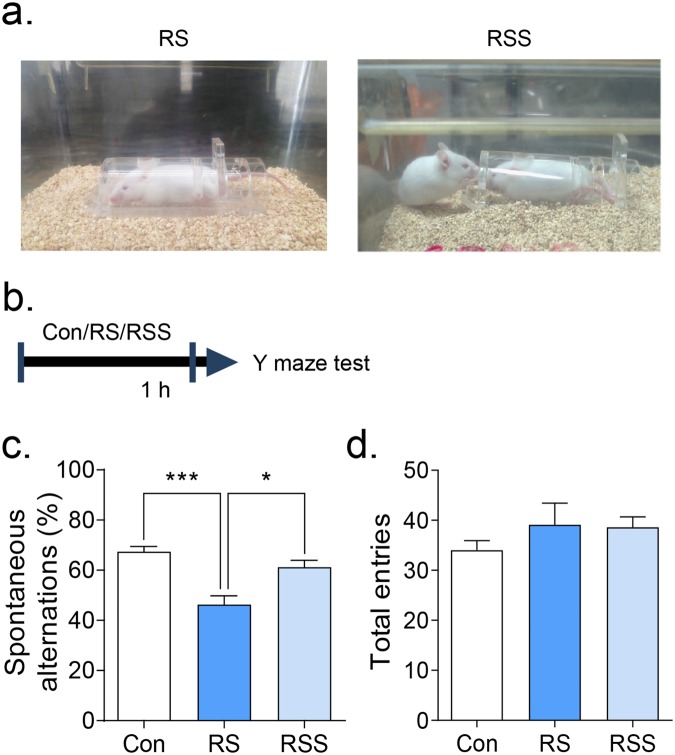
Figure 1.
Social interaction rescued the restraint stress-induced working memory impairments. (a) Images representing restraint stress (RS) and restraint stress with the presence of conspecific mouse (RSS) conditions. (b) Scheme of Y maze test performed after an hour of RS or RSS. (c) Spontaneous alternations and (d) total arm entries were evaluated in the Y maze test (n = 10). All data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M using bar graphs. (c) one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison post hoc analysis and (d) Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post hoc analysis. * is p < 0.05, *** is p < 0.001. Con: vehicle control group, RS: restraint stress group, RSS: restraint stress with social interaction group.