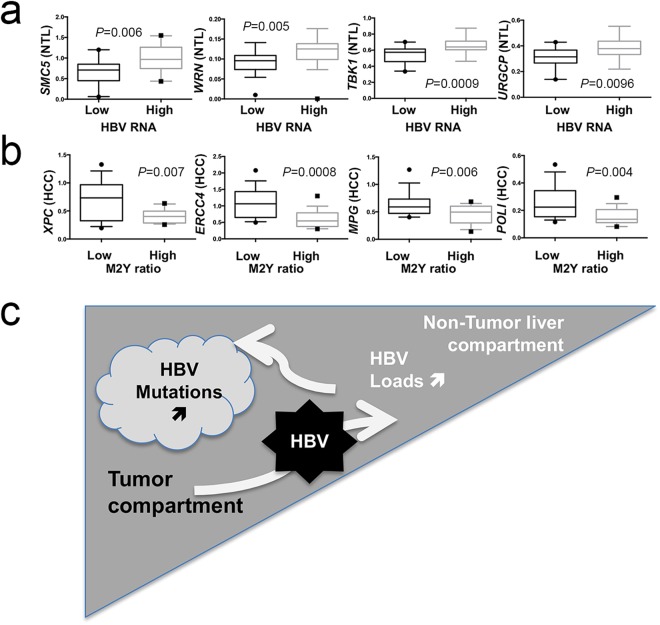
Figure 7.
DNA repair gene expression correlates with HBV read-outs. (a,b) Box-and-whiskers plots. (a) Expression of four DNA repair genes stratified according to the median of HBV RNA expression in NTL (low expression group, n = 18, high expression group, n = 17). From right to left: structural maintenance of chromosome 5 (SMC5); Werner syndrome RecQ like helicase (WRN); TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1); up regulator of cell proliferation (URGCP). (b) Expression of four DNA repair genes stratified according to the median proportion of mutated monotonous di-pyrimidines (M2Y = CpC or TpT, low mutated M2Y ratio, n = 15, high ratio, n = 17). From right to left: complex subunit, DNA damage recognition and repair factor (XPC); excision repair 4, endonuclease catalytic subunit (ERCC); N-methylpurine DNA glycosylase (MPG); DNA polymerase iota (POLI). Statistical tests for comparison were either Student t test or Mann-Whitney U test depending on the distribution of values as assessed by a F-test. (c) Graphical abstract proposal for a two-compartment model (i.e. HCC and NTL) explaining viral loads and mutations in Peruvian patients with HCC.