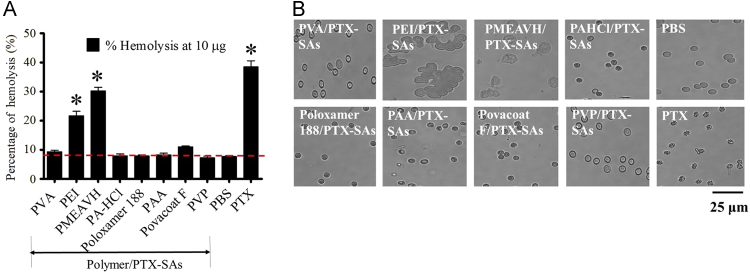
Figure 2.
Evaluation of hemocompatibility behavior of Poly/PTX-SAs. (A) Hemocompatibility was assessed using human red blood cells by treating them for 1 h with PTX or Poly/PTX-SAs. In this experiment, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, 1 mg/mL) served as a positive control (100% lysis) while 1× PBS was used as a negative control (0%). The percentage of hemolysis was calculated using our previously reported method. (B) Images of treated red blood cells on glass slide were captured using EVOS® FL Imaging System (AMF4300, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). PVP/PVA-PTX-SAs demonstrate intact membrane morphology in RBCs as PBS, whereas PTX and other Poly/PTX-SAs exhibited toxic behavior by disintegrating membrane structure of RBCs (Bar=25 μm). Data represented as mean±standard error of the mean (n=3), *P<0.05.