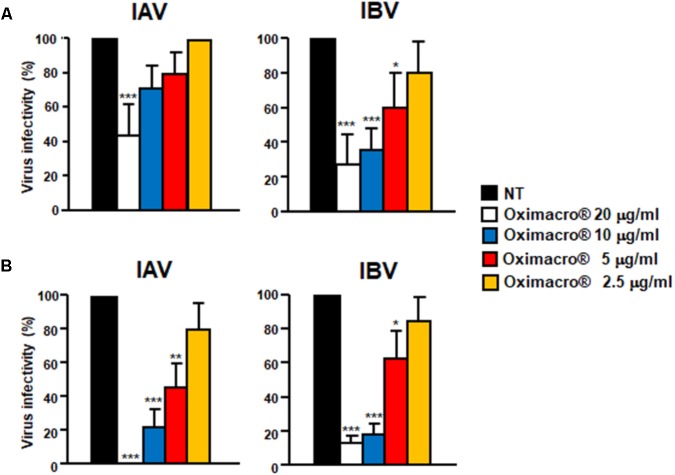
FIGURE 3.
IV attachment and entry is prevented by Oximacro®. (A) Oximacro® affects IV attachment. Prechilled MDCK cells were infected with precooled IAV or IBV (40 PFU/well) in the presence of different concentrations of Oximacro® (20-10-5-2.5 g/ml) at 4°C for 2 h. After viral adsorption, the cells were washed and overlaid with 0.7% Avicel. At 48 h p.i., viral plaques were stained and microscopically counted. The results shown are means ± SD (error bars) from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. (B) Oximacro® inhibits IV entry. Prechilled MDCK cells were infected with IAV or IBV (40 PFU/well) for 2 h at 4°C to allow virion attachment to the cells. After adsorption, the cells were treated with different concentrations of Oximacro® (20-10-5-2.5 μg/ml) for 2 h at 37°C, prior to inactivation of extracellular virus with acidic glycine buffer for 30 s at RT. After further washing, the cells were incubated with medium-containing 0.7% Avicel. At 48 h p.i., viral plaques were stained and microscopically counted. The results shown are means ± SD (error bars) of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗p < 0.05 compared with the 100% virus infectivity of untreated controls.