FIGURE 8.
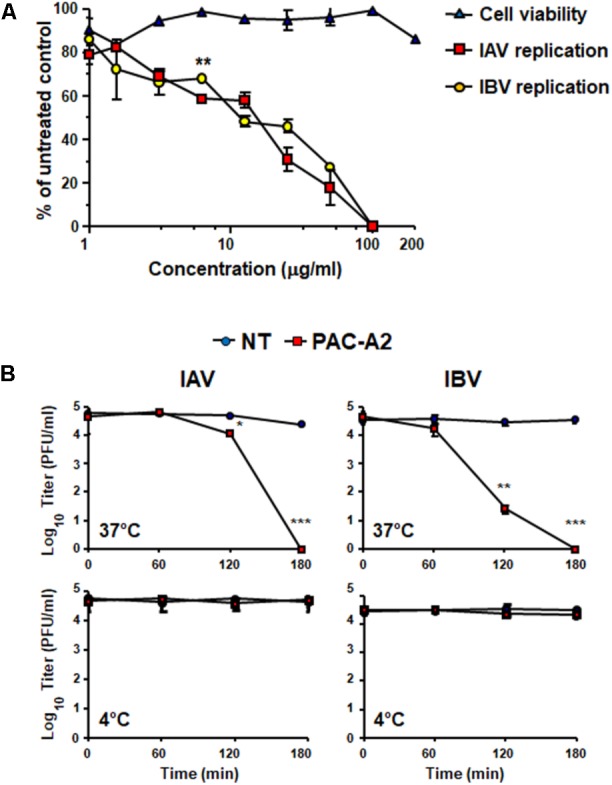
Purified PAC-A2 inhibits IV replication by causing loss of virion infectivity. (A) PAC-A2 inhibits replication of IAV and IBV. MDCK cell were infected with either IAV or IBV (40 PFU/well), and, where indicated, the cells were treated with increasing concentrations of PAC-A2 1 h before, during virus adsorption, and after adsorption throughout the experiment. At 48 h p.i., plaques were stained and microscopically counted. To determine cell viability, MDCK cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of PAC-A2, and the number of viable cells was determined by the MTT method. Statistical analysis was accomplished by comparing IAV and IBV replication curves. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗p < 0.05. (B) Treatment with PAC-A2 abolishes the infectivity of IV particles. IAV or IBV (2 × 104 PFU) were incubated at 37°C (A) or at 4°C (B) for various lengths of time in the absence (closed circles) or in the presence of 50 μg of PAC-A2 (closed squares). After incubation, the samples were diluted to reduce PAC-A2 below that which inhibits IV replication and the residual infectivity assessed by plaque assay. The mean plaque counts were expressed as PFU/ml on a log10 scale. The data shown represent means ± SD (error bars) of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗p < 0.05 compared with the titer of untreated controls (NT).
