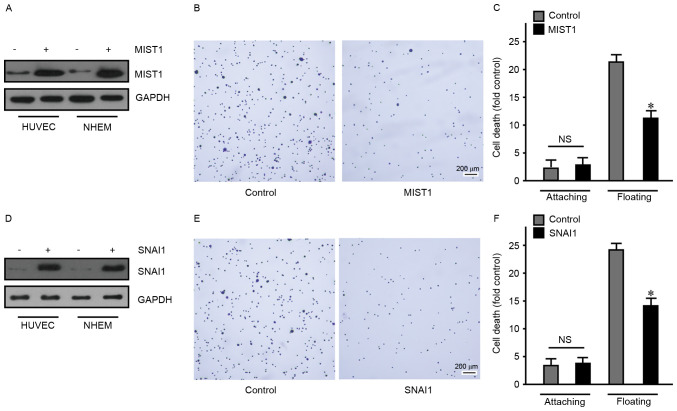
Figure 2.
MIST1 and SNAI1 disrupt cell-matrix adhesion and promote anchorage independence. (A) MIST1 was ectopically expressed in HUVEC and NHEM 2493 cell lines and confirmed by western blot analysis. (B) Overexpression of MIST1 reduced the adhesion ability of HUVEC (scale bar, 200 µm). (C) MIST1 enhanced the viability of HUVEC in suspension culture, indicating bypassing of anoikis. (D) SNAI1 was ectopically expressed in HUVEC and NHEM 2493 cell lines and confirmed by western blot analysis. (E) Overexpression of SNAI1 reduced the adhesion ability of HUVEC (scale bar, 200 µm). (F) SNAI1 enhanced the viability of HUVEC in suspension culture, indicating bypassing of anoikis. Findings for NHEM 2493 were similar, data not shown. NS, no significance; *P<0.05 vs. control. MIST1, muscle intestine and stomach expression 1; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; NHEM 2493, normal human epidermal melanocytes.