Figure 4.
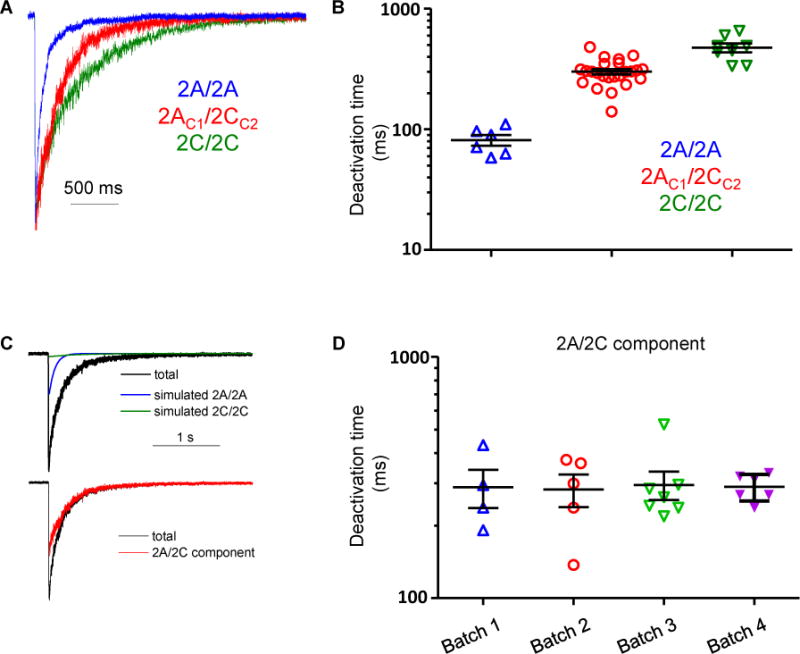
Glutamate deactivation time courses of diheteromeric and triheteromeric NMDARs. A. Normalized representative current responses to brief (<5 ms) application of 1 mM glutamate in the continuous presence of 100 μM glycine from outside-out patches excised from oocytes expressing of GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2A (blue), GluN1/GluN2AC1/GluN2CC2 (red), or GluN1/GluN2C/GluN2C (green). B. Deactivation time constants for GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2A and GluN1/GluN2C/GluN2C receptors were obtained by fitting the time course with a single exponential function. Deactivation time constants for GluN1/GluN2AC1/GluN2CC2 receptors were obtained by fitting the response time course with the sum of three exponential functions. C. The total response from GluN1/GluN2AC1/GluN2CC2 receptors is shown with the GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2A and GluN1/GluN2C/GluN2C receptor components, which were simulated using the deactivation time constant determined from oocytes expressing GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2A and GluN1/GluN2C/GluN2C receptors. The amplitudes of the diheteromeric contribution to the time course were set as the escape current measured from GluN1/GluN2AC1/GluN2AC1 and GluN1/GluN2CC2/GluN2CC2 receptors. The GluN1/GluN2AC1/GluN2CC2 receptor component was isolated by subtracting the GluN1/GluN2A/GluN2A and GluN1/GluN2C/GluN2C receptor components from the total current. D. Summary of deactivation time constants for the GluN1/GluN2AC1/GluN2CC2 receptor component determined from 4 different batches of oocytes.
