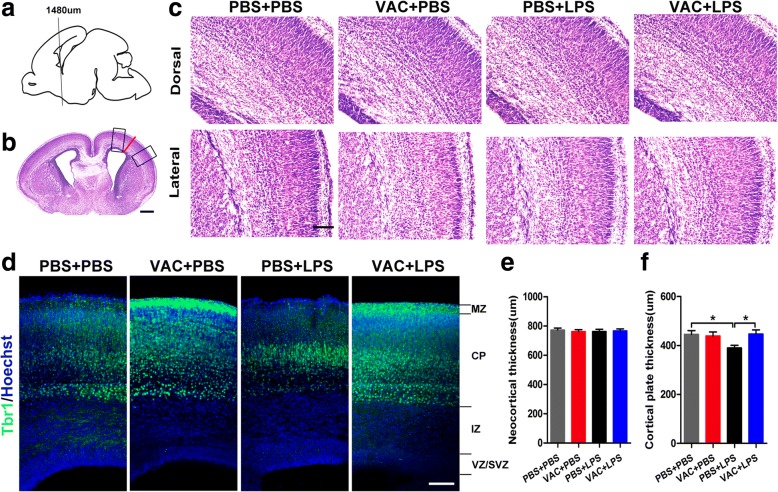
Fig. 5.
Maternal VAC and MIA effects on the thickness of the neocortex and cortical plate (CP) at E18.5. a Coronal sections of embryonic brains at 1480 μm from the front of the olfactory bulb were analyzed. b Coronal sections were Nissl stained. Dorsal and lateral regions are marked by the rectangles, and neocortical thickness is marked by the red line. c The dorsal and lateral views of the cortex are shown as the positions of the rectangles in a. d Coronal sections of the indicated embryonic brains at 1480 μm were immunostained with Tbr1 antibody (green) and Hoechst (nuclei). e There were no differences in neocortical thickness among the four groups. f A two-way ANOVA of CP thickness showed an interaction effect of MIA × VAC (F1,20 = 4.467, p = 0.047), and post hoc comparisons confirmed that MIA decreased the cortical plate thickness compared to that in controls (p = 0.016) and that VAC pretreatment restored the thickness to a normal level (p = 0.014). n = 6 mice/group; *p < 0.05 (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test). The results are all shown as the mean + s.e.m. Scale bars, 500 μm in b, 100 μm in c–d