Fig. 7.
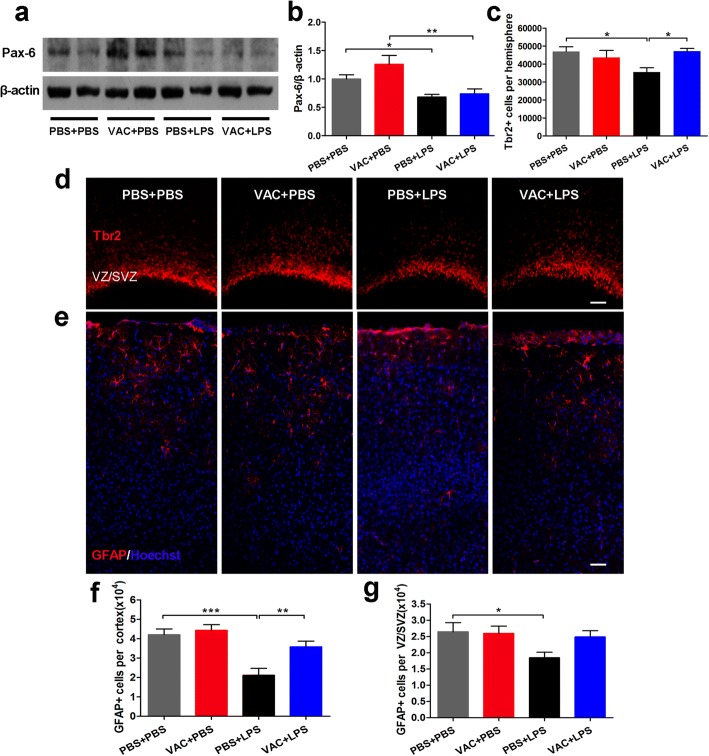
Maternal VAC and MIA effects on neural precursor cells in the embryonic cortex at E18.5 and astrocytes in the adult cortex at 6 weeks. a Representative Western blot bands of Pax-6 and β-actin. b The ratio of Pax-6 to β-actin was quantified. ANOVA showed a significant main effect of MIA (F1,12 = 17.899, p = 0.001) on Pax-6 concentration, and post hoc comparisons revealed that MIA reduced the Pax-6 concentration (p = 0.042) and that VAC pretreatment failed to rescue that effect (p > 0.05). d Coronal sections of E18.5 mouse brains were immunostained with Tbr2 (red), and VZ/SVZ images were obtained. c The number of Tbr2+ cells per hemisphere was counted. ANOVA showed an interaction effect between MIA and VAC (F1,12 = 7.252, p = 0.02), and post hoc comparisons confirmed that MIA decreased the number of Tbr2+ cells (p = 0.013) and that VAC pretreatment reversed the decrease (p = 0.012). e Coronal sections of 6-week-old mouse brains were immunostained for GFAP (red) and Hoechst (blue). Cortical images are shown. f There are significant main effects of MIA (F1,12 = 22.412, p = 0.0004) and VAC (F1,12 = 7.395, p = 0.019) for GFAP+ cells. Post hoc comparisons showed that MIA induced a significant reduction of astrocytes in the cortex (p < 0.001) and that VAC pretreatment prevented the effect (p = 0.006). g A trend toward a similar effect for the VZ/SVZ was also observed. n = 4 mice/group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test). The results are all shown as the mean + s.e.m. Scale bars, 50 μm in (d, e)