Fig. 3.
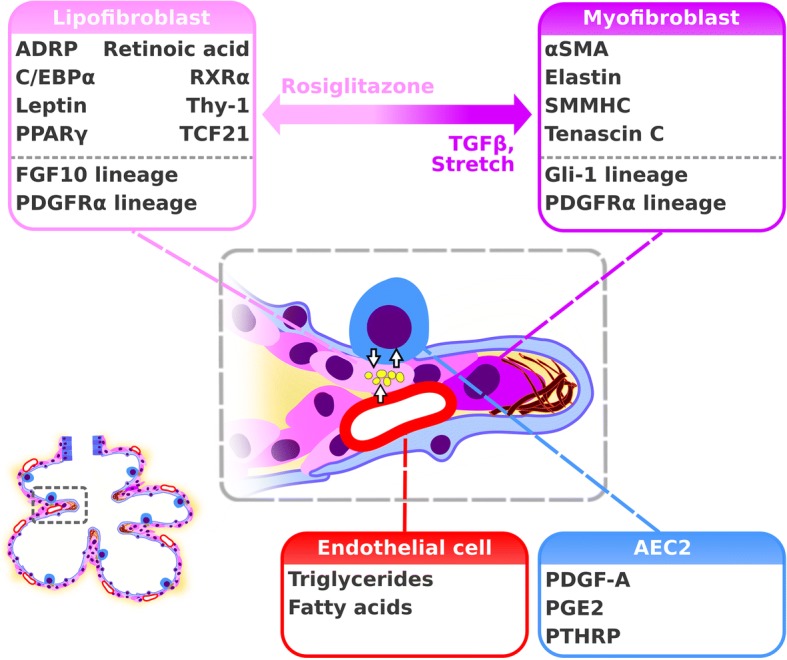
Lipogenic versus myogenic fibroblast phenotype. Lipogenic (lipofibroblast) and myogenic (myofibroblast) fibroblasts differentiate during early lung development and the saccular stage. Lipofibrobasts support alveolar epithelial type II cells (AECII) cell function via an intercellular crosstalk mediated by stretch, parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHRP), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and leptin while myofibroblasts produce extracellular matrix molecules such as elastin. Activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR)γ by Rosiglitazone promotes the lipogenic phenotype. Stretch and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β induce the myogenic phenotype
