Figure 1.
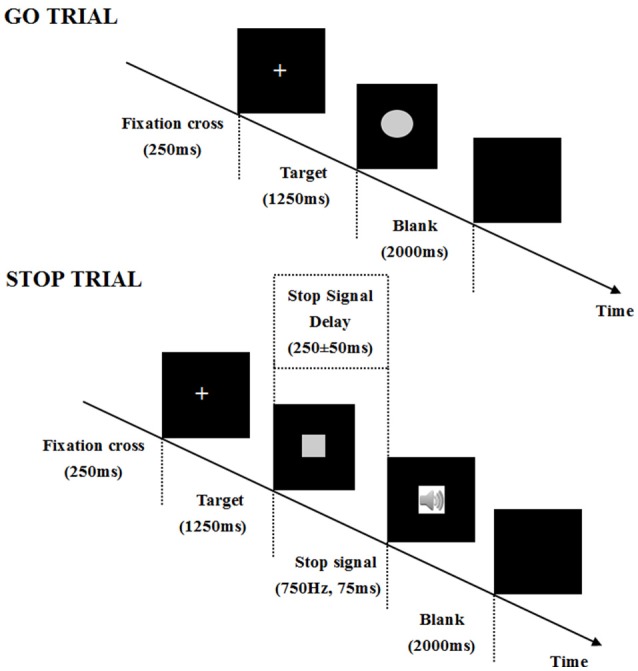
Depiction of a go and a stop trial course in the stop-signal task. In this paradigm, subjects are asked to perform an auditory two-choice reaction task. In the go trials, participants need discriminate the shape of a stimulus (a square corresponds to a left response “Q” and a circle corresponds to a right response “P”). Each trial begins with a central fixation cross (250 ms), then a square or circle is presented for 1,250 ms in a randomized order. The inter-trial interval is a blank screen of 2,000 ms. In the stop trials, occasionally, a tone (i.e., the stop-signal, 750 Hz, 75 ms) is presented shortly after the stimuli onset (a square or circle). Subjects are instructed to withhold their response when the tone occurs. In the stop-signal trials, the stop-signal is presented after a variable stop-signal delay (SSD; i.e., the delay between the onset of a go stimulus and the onset of a stop-signal). SSD is initially set at 250 ms and is adjusted dynamically with the staircase tracking procedure: when inhibition is successful, SSD increases by 50 ms; when the inhibition is unsuccessful, SSD decreases by 50 ms.
