Fig. 3.
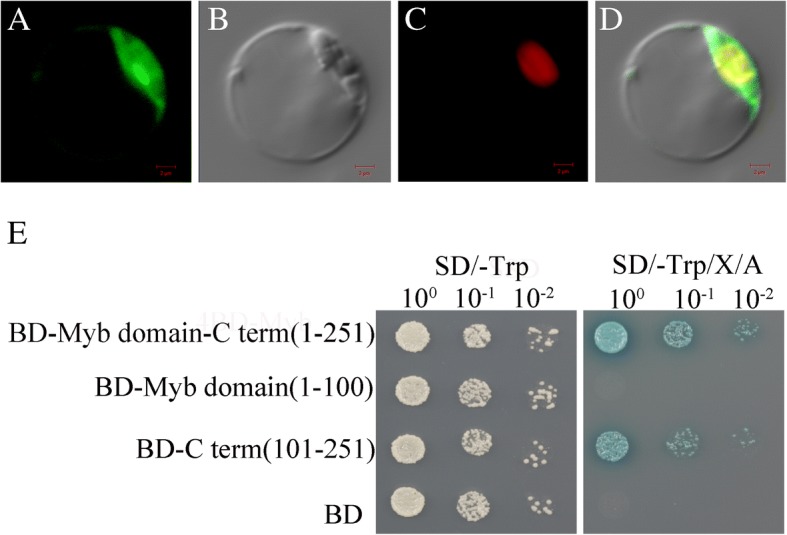
Subcellular localization and transactivation analysis of OsPHL3. a Subcellular localization of OsPHL3-GFP fusion protein under the control of CaMV35S promoter. b Bright field. c The nuclear marker mCherry-VirD2NLS vector (mCherry). d Merged image. Bar = 2um from A to D. (E) OsPHL3 full-length coding region, N-terminal region containing Myb-DNA binding domain (1–100 amino acids) or the C-terminal region containing CC binding domain (101–251 amino acids) were individually inserted into pBD-GAL4 DNA binding-domain contained plasmid. The empty pBD vector was used as control. The expression of OsPHL3 coding region and OsPHL3-C terminal showed resistance to toxic drug Aureobasidin A
