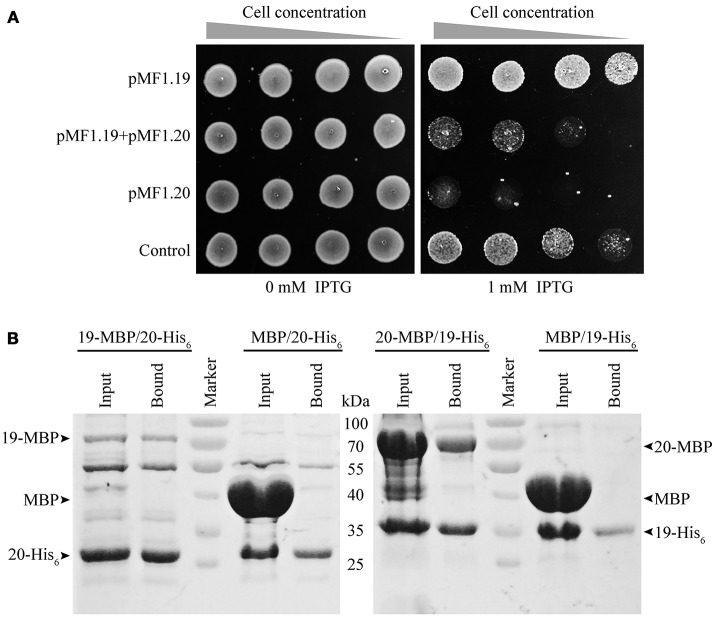
Figure 3.
Results of in vivo and in vitro experiments with pMF1.19 and pMF1.20. (A) Growth abilities of the BL21 strains containing empty pMAL-c5x and pACYC-Duet plasmid (control), pMF1.20-harboring plasmid and empty pACYC-Duet, 19-pACYC and empty pMAL-c5x, and the two pMF1.19- and pMF1.20-harboring plasmids. The medium was with or without IPTG supplementation. Equal numbers of BL21 cells were five-fold serially diluted and spotted on the plates. Pictures were taken after overnight cultivation. (B) Pull-down experiments on the binding activities between pMF1.19 and pMF1.20. 19-MBP (71 kDa) and 20-MBP (69 kDa) were purified by amylose resin and 19-His6 (31 kDa) and 20-His6 (29 kDa) were purified by Ni2+ beads. 19-MBP (1.9 mg/ml, 300 μl) was incubated with 20-His6 (1.5 mg/ml, 300 μl). In a similar manner, 20-MBP (7 mg/ml, 150μl) was mixed with 19-His6 (1.5 mg/ml, 450 μl). MBP protein was incubated with 19-His6 or 20-His6 as negative controls. The input and bound samples were tested using SDS-PAGE. The PageRulerTM Prestained Protein Ladder was used.