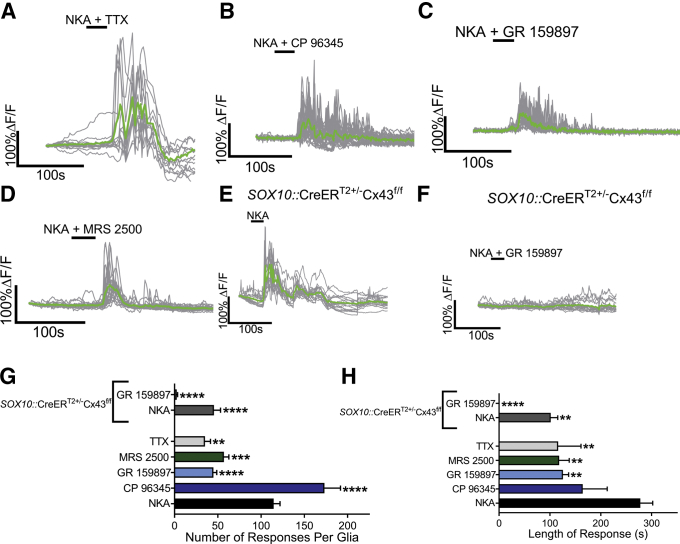
Figure 5.
Glial Ca2+responses driven by NKA require the activation of NK2Rs and purinergic intercellular signaling mediated by Cx43. (A–D) Representative glial Ca2+ responses evoked by NKA in the presence of (A) tetrodotoxin, (B) the NK1R antagonist CP 96345, (C) the NK2R antagonist GR 159897, or (D) the P2Y1R antagonist MRS 2500. Gray traces show the responses of individual glial cells, and the averaged response of all glia within the ganglion is shown in the green trace. (E and F) Representative glial Ca2+ responses evoked by NKA in tissues from SOX10::CreERT2+/-Cx43f/f mice in the (E) absence or (F) presence of GR 159897. (G and H) Quantification of the effects of CP 96345, GR 159897, tetrodotoxin, MRS 2500, or ablation of glial Cx43 in SOX10::CreERT2+/-Cx43f/f mice on the (G) number and (H) length of response of glial Ca2+ responses induced by NKA (n = 15–33 glia from 3 to 5 mice; 1-way analysis of variance; **P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ****P < .0001). TTX, tetrodotoxin.