Figure 2.
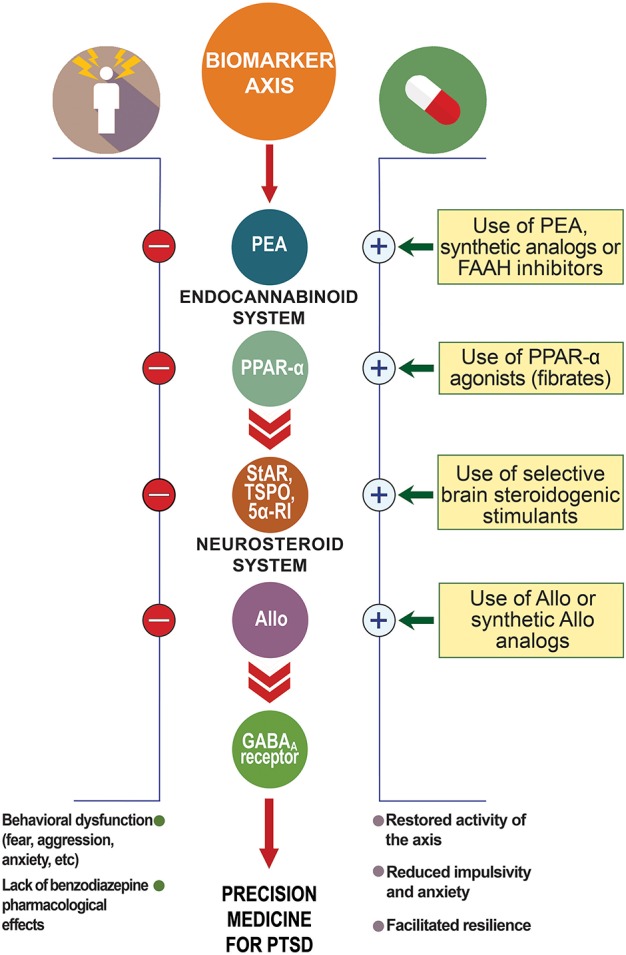
Biomarker axis at the interface of the endocannabinoid and neurosteroid systems. In animal models of PTSD, protracted stress results in the downregulation of allopregnanolone biosynthetic enzymes (e.g., 5α-reductase type I, 5α-RI) and allopregnanolone concentrations in corticolimbic glutamatergic neurons of the frontal cortex, hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala. This allopregnanolone decrease correlates with behavioral dysfunction, such as increased aggression, enhanced contextual fear responses and anxiety-like behavior (Pinna et al., 2003; Pibiri et al., 2008). Supplying allopregnanolone or stimulating its biosynthesis decreases anxiety-like behavior, aggression and fear responses (Pinna, 2013; Pinna and Rasmusson, 2014). Stress may also result in changes in GABAA receptor subunit expression (Pinna et al., 2006; reviewed in Locci and Pinna, 2017a) with increased α4, α5, and δ subunits and decreased α1, α2, and γ2, which result in down-regulated benzodiazepine binding sites and inefficacy of benzodiazepine pharmacological action (Pinna et al., 2006; Nin et al., 2011b). Protracted stress results in increased GABAA receptor subunits, including α4−5,β,δ highly sensitivity for allopregnanolone (Locci and Pinna, 2017a). Both allopregnanolone biosynthesis downregulation and decreased benzodiazepine binding sites have been reported in PTSD patients (Rasmusson et al., 2006, 2018; Geuze et al., 2008). Thus, the combination of downregulation of allopregnanolone biosynthesis, changes in GABAA receptor subunit expression, and lack of benzodiazepine pharmacological action are peculiar changes observed in PTSD that may provide a selective biomarker axis for this disorder. Stress may affect PEA levels and expression of PPAR-α, which in turn may downregulate allopregnanolone concentrations. Thus, the PPAR-α-allopregnanolone axis may provide further biomarker candidates to support selection of the best individualized precision medicine for PTSD. Allo, allopregnanolone; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; PEA, N-palmitoylethanolamine; PPAR-α, peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor-α; StAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein; TSPO, 18 kDa translocator protein.
