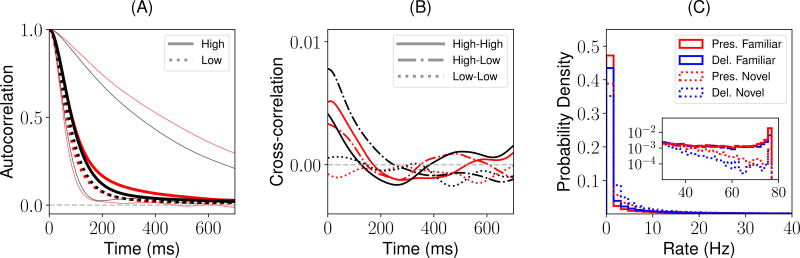
Figure 7.
Statistical properties of the chaotic background and retrieval states, for a network with parameters as in Fig 6. (A) Red: background state. Black: retrieval state. Thick traces: mean autocorrelation (AC) functions across 100 randomly sampled neurons with mean firing rate between 1Hz and half of the maximal firing rate (low mean firing rates; dashed) and between half of the maximal firing rate and 65Hz (high mean firing rates; solid). Light traces: AC function for neurons with the fastest and slowest decays, showing a broad range of individual AC timescales. (B) Mean cross-correlation (CC) functions across 200 randomly chosen pairs of neurons with high (i.e. high-high), low (i.e. low-low) and with one neuron high and the other low (i.e. high-low) mean firing rates. Same color code than panel A. (C) Distribution of mean firing rates during the presentation (red) and delay (blue) periods for novel (dashed) and familiar (solid) stimuli.