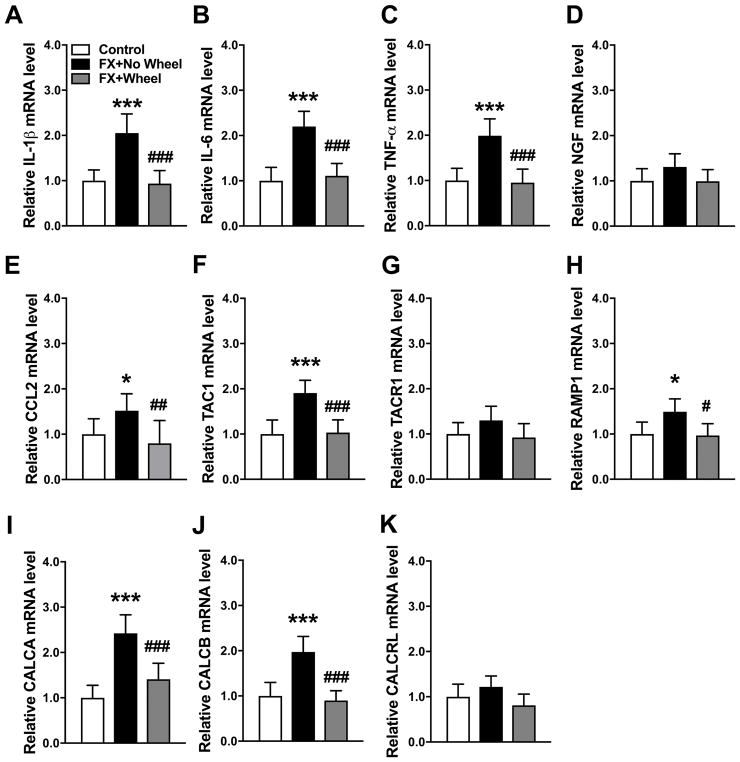
Figure 5. The effects of exercise on post fracture gene expression of spinal cord inflammatory mediators.
Inflammatory mediator expression in the lumbar cord innervating the fracture limb was measured by real-time PCR. IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, CCL2, TAC1, RAMP1, CALCA and CALCB (A–C, E–F, H–J) gene expression were up-regulated at 7 weeks post fracture (FX+No Wheel), compared to nonfractured control mice (Control). All these increases were reversed by voluntary wheel running for 4 weeks starting at day 21 after fracture (FX + Wheel). There were no changes in the hindpaw skin expression of NGF (D), TACR1 (G) and CALCRL (K) at 7 weeks post fracture, compared to nonfracture control mice, and exercise had no effects on the post fracture expression of NGF, TACR1, or CALCRL. Values are means ± SD, n=8 per cohort. One-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post hoc testing. * P< 0.05, ** P< 0.01, *** P< 0.001 for FX+No Wheel or FX + Wheel vs Control, # P< 0.05, ## P< 0.01, ### P< 0.001 for FX + Wheel vs FX+No Wheel.