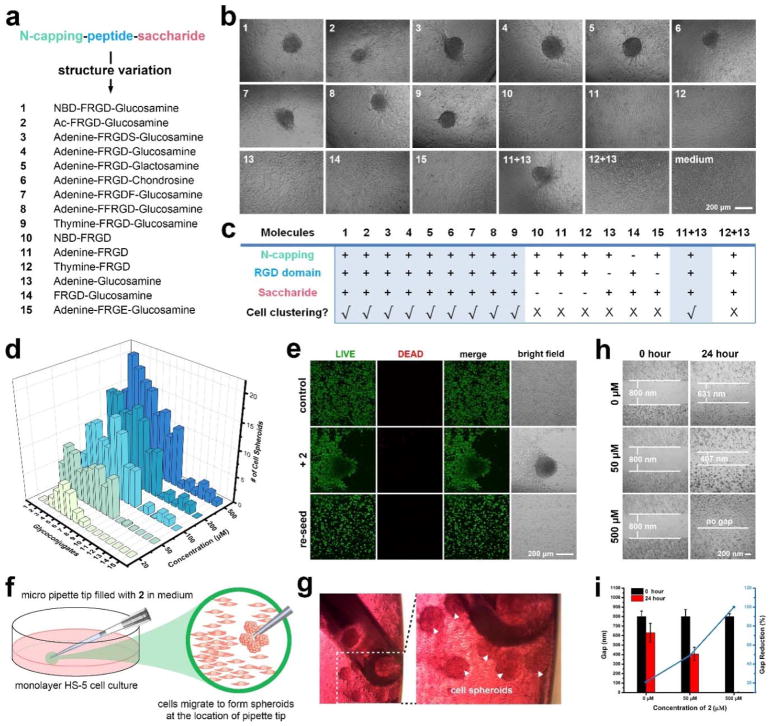
Figure 4.
Multifunctional small glycopeptides containing N-terminal capping, glycosylation and RGD integrin-binding domain enable cell spheroids. (a) The architecture of multifunctional small glycopeptides and the control analogs (see Scheme 2 for specific chemical structures). Ac: acetyl; F: phenylalanine; R: arginine; D: aspartic acid; S: serine; E: glutamic acid; NBD: 2-(4-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazol-7-yl)-; (b) Optical images of HS-5 cells incubated with different molecules (1-15) at the concentration of 50 μM for 24 hours. The initial cell number is 3.0×104/well in a 96-well plate. The scale bar is 100 μm. Molecules 1-9 alone and 11+13 combination are able to induce HS-5 cell clustering. (c) Table summary regarding chemical structures v.s. spheroids, indicating the importance of N-terminal capping, glycosylation, and integrin-binding domain for the observed in vitro morphogenesis. (d) Quantification of the numbers of HS-5 clusters formed after the treatment of different small molecules (1-15) at multiple concentrations (20, 50, 100, 200, 500 μM) for 24 h. The initial cell number is 3.0×104/well in a 96-well plate. (e) LIVE/DEAD cell assay of HS-5 cells treated with medium only, 2 (100 μM) in medium, and HS-5 cells in spheroids being lysed and reseeded. The incubation time is 24 hour. The initial number of cells is 5.0×105/well in a 35-mm confocal dish. The scale bar is 100 μm. (f) (g) Schematic illustration and optical images of HS-5 spheroids selectively form at the location of the micropipette tips (filled with medium containing 500 μM compound 2). (h) (i) Cell migration assay of monolayer HS-5 cells (80 % confluence) treated with 2 (50 and 500 μM). The size of the gap was measured both before and after incubation with 2 for 24 hours.