Figure 5. Discovery of Novel Sedative-Hypnotics Using Zebrafish Larvae Photomotor Responses.
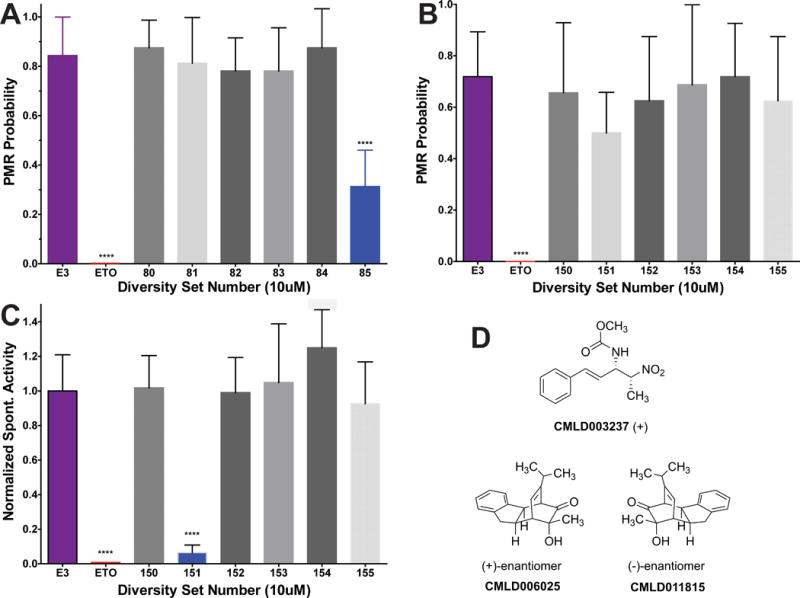
A-C) Bars represent cumulative photomotor response (PMR) probability or normalized spontaneous activity from 4 trials at 3 min intervals (mean with symmetrical 95% CI; n =8). A) Screening PMR results from an experiment including negative (E3 with 0.2% DMSO) and positive (10 μM etomidate; ETO) control groups, and 6 groups of larvae exposed to test compounds at 10 μM. Diversity Set #85 (DS85; CMLD003237) inhibits larval photomotor responses by over 60% (p < 0.0001 by unpaired Student’s t-test). B) Screening PMR results for DS150 through DS155 are shown. Note that DS151 (CMLD006025) does not significantly inhibit PMR probability (p = 0.045 by unpaired Student’s t-test, above the p = 0.0024 significance threshold after Bonferroni correction for 7 comparisons). C) Spontaneous activity, normalized to that of the negative control group from the same experiment shown in panel B. DS151 (CMLD006025) inhibited spontaneous activity by over 90% (p < 0.0001 by Student’s t-test). D) Chemical structures of CMLD003237, CMLD006025, and CMLD011815, the (-)- enantiomer of CMLD006025, are shown. **** p < 0.0001.
