Figure 5. Parasympathetic cholinergic innervation of vertebrobasilar arteries is reduced in the hypertensive rat.
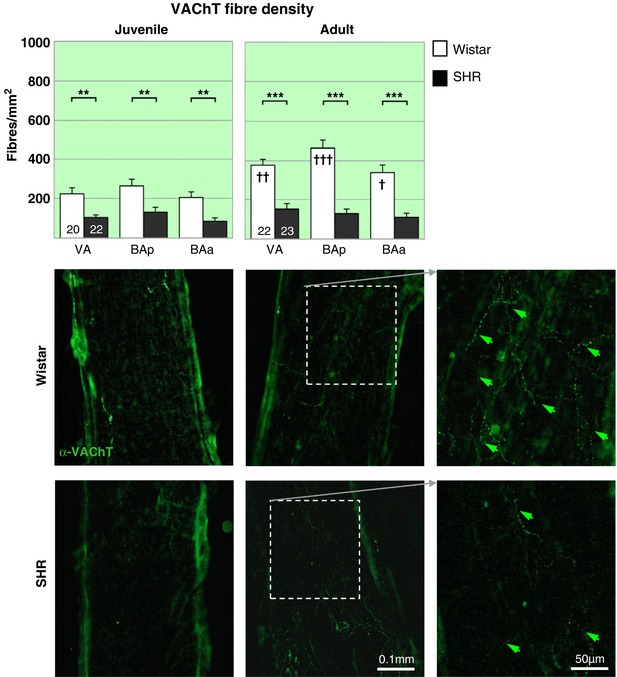
A dramatic deficit in cholinergic parasympathetic labelling (α‐VAChT) is evident in both PHSH (top) and SH rats (▪) compared to age‐matched Wistar rats (▫) across the 3 regions. Notably the decrease is prior to the onset of hypertension. The two‐way RM‐ANOVA reveals a highly significant effect of strain (P < 0.001) and a significant effect of region (P < 0.05) for both age groups. Post hoc analyses found the effects significant (P < 0.001) in all regions. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. Within strain comparisons found significant difference in fibre densities in the Wistar rats across age (P < 0.001) and with respect to region (P < 0.001), post hoc differences across regions are indicated by † on the adult panel. † P < 0.05, †† P < 0.01, ††† P < 0.001. No differences could be found between the two groups of SH rats. Representative fluorescence microscopy images of area BAp for each group labelled with the cholinergic parasympathetic marker α‐VAChT‐488, including excerpts of adult innervation at higher magnification (far right). [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
