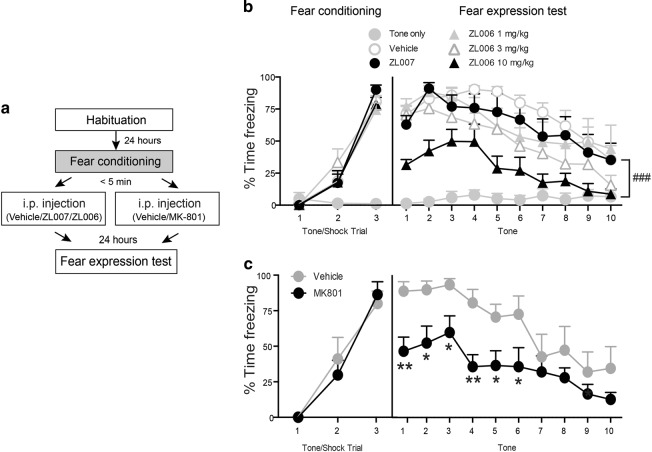
Fig. 1. Systemic disruption of PSD95/nNOS interaction and inhibition of NMDAR impaired consolidation of auditory Pavlovian fear conditioning.
a Schematic of the behavioral protocol. Immediately after fear conditioning, rats were given i.p. injections of indicated treatments. The retention of conditioned fear memory was tested 24 h later. b The five groups of animals that had tone/shock pairings showed normal cued fear acquisition (Trial: F2, 56 = 299.4, P < 0.0001). In the fear expression test, 10 mg/kg ZL006 treated animals (n = 8) displayed significantly decreased freezing responses when compared with vehicle controls (n = 7) (post hoc test: t = 3.77, DF = 28, P < 0.001). ### P < 0.001 ZL006 10 mg/kg vs. vehicle; Groups with lower doses of ZL006 (1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg, n = 6) and ZL007 group (n = 6) showed similar levels of freezing during fear expression compared to the vehicle group (P > 0.05). Rats in “Tone only” group (n = 7) did not freeze to the CS in neither fear training nor fear expression test. c Both vehicle (n = 7) and MK-801 (n = 7) treated animals showed normal cued fear acquisition (Trial: F2, 24 = 59.62, P < 0.0001). However, MK-801 treated animals showed significantly decreased freezing responses in fear expression test (Treatment: F1, 12 = 8.550, P < 0.05). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 relative to vehicle group