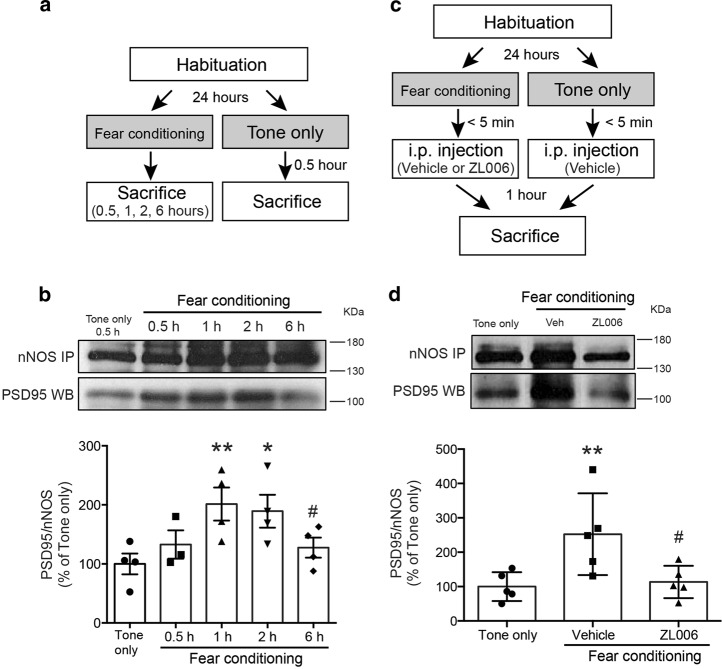
Fig. 3. Fear conditioning induces a robust increase in amygdala PSD95/nNOS binding, which is prevented by pretreatment of ZL006.
a Schematic of the behavioral protocol. Rats were habituated to the conditioning box, fear conditioned with 3 tone/shock pairings and sacrificed either 0.5, 1, 2, or 6 h following conditioning. The “Tone only” group did not receive shock and were sacrificed 0.5 h after non-shock training. b Protein extracts from BLA were immunoprecipitated with nNOS antibody and immunoblotted with PSD95 antibody (top, representative blots). Levels of PSD95/nNOS ratio were expressed as a percentage of those in “Tone only” controls (n = 3 or 4, F4, 14 = 3.526, P < 0.05) (bottom). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 relative to “Tone only” group; # P < 0.05 relative to 1 h group. c Schematic of the behavioral protocol. Immediately after fear conditioning, rats received i.p. injections of either vehicle or 10 mg/kg ZL006 and were sacrificed 1 h after fear conditioning. d Protein extracts from BLA were immunoprecipitated with nNOS antibody and immunoblotted with PSD95 antibody (top, representative blots). Levels of PSD95/nNOS ratio were expressed as a percentage of those in “Tone only” controls (n = 5, F2, 12 = 5.895, P < 0.05) (bottom). **P < 0.01 relative to “Tone only” group; # P < 0.05 relative to vehicle group