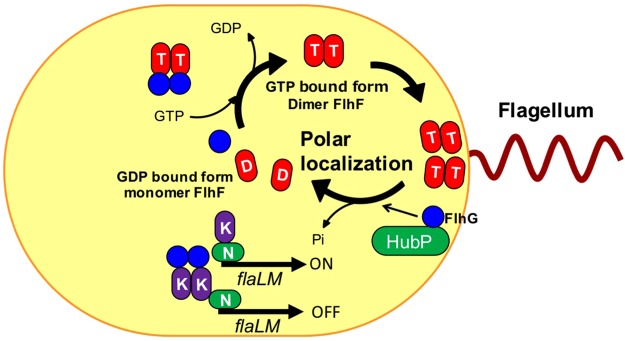
Figure 7.
The model of FlhF polar localization in V. alginolyticus. FlhF diffuses into the cytoplasm as a GDP-bound monomer (shown as the red ellipse with “D”), but when it binds to GTP (shown as the red ellipse with “T”), it forms a dimer and becomes localized to the pole. Localized FlhF promotes flagellar formation at cell pole. FlhG diffuses in the cytoplasm and interacts with FlhF to inhibit polar localization of FlhF. Also, FlhG binds to FlaK (shown as the purple ellipse with “K”) to inhibit the early class of flagellar genes (flaLM), whose expression is dependent on FlaK and RpoN (shown as the green ellipse with “N”). At the poles, the GTPase activity of FlhF is activated by FlhG, which is localized to the pole by the HubP scaffold. FlhF is converted to the GDP bound form and dissociates from the cell pole. In the wild type V. alginolyticus, the amount of FlhF localized at the pole is controlled to a level resulting in biosynthesis of a single, polar flagellum.