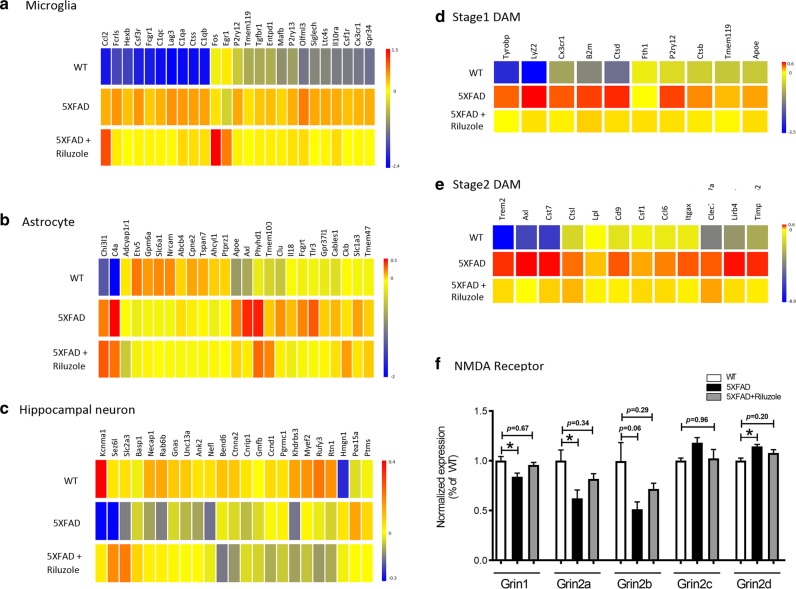
Fig. 4. Expression changes in cell-type-specific markers and hippocampal NMDA receptor subunits are reversed by riluzole treatment.
Heatmap showing 23–25 canonical expression markers for hippocampal (a) microglia39, b astrocytes39, c neurons39, and (d, e) a unique population of disease-associated microglia (DAM)40. Riluzole showed a rescue effect in neuronal and astrocytic populations. The rescue was most pronounced in microglia-related genes, and in particular DAM, which are associated with neurodegeneration. f 5XFAD mice have a significantly decreased expression levels of NMDA subunits Grin1 (p = 0.0417) and Grin2a (p = 0.0453), a trend towards reduced Grin2b (p = 0.065), and increased levels of Grin2d (p = 0.0251) in comparison to wild-type animals. Riluzole modulated the NMDA subunits expression levels in 5XFAD mice to WT control levels (5XFAD-Riluzole vs. WT; Grin1, p = 0.6764, Grin2a, p = 0.3420, Grin2b, p = 0.2969, Grin2c, p = 0.9620, Grin2d, p = 0.2059. The RNA-Seq data are based hippocampal tissue pooled into three replicate sequencing libraries/group from WT, n = 10 (pooled 3, 3, 4 mice); 5XFAD, n = 7 (pooled 2, 2, 3 mice); and 5XFAD-Riluzole, n = 8 (pooled 2, 3, 3 mice). *p < 0.05