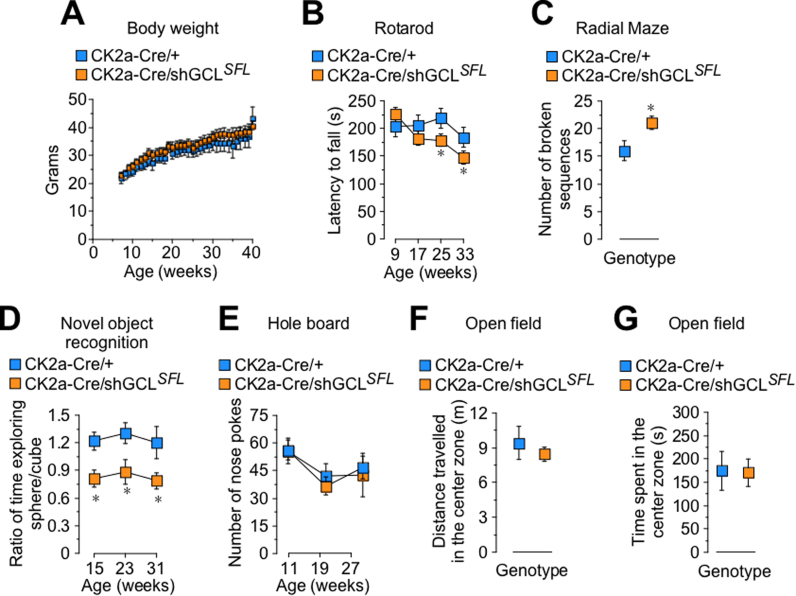
Fig. 4.
Knock down of GCL in vivo triggers behavioral signs of cognitive decline. (A) Body weight was unaltered in CK2a-Cre/shGCLSFL male mice when compared with their controls (CK2a-Cre/+). (B) Age-dependent decline in the performance of the rotarod test in CK2a-Cre/shGCLSFL mice. (C) Higher number of broken sequences in the radial arm maze test in CK2a-Cre/shGCLSFL mice. (D) Lower performance at the novel object recognition test in CK2a-Cre/shGCLSFL mice. (E) Unaltered number of nose pokes in the Hole board test in CK2a-Cre/shGCLSFL mice. (F,G) Unaltered distance travelled and time spent in the central zone of the Open field test in CK2a-Cre/shGCLSFL mice. Data are mean ± SEM values (n = 6). *p < 0.05 (Student's t-test).