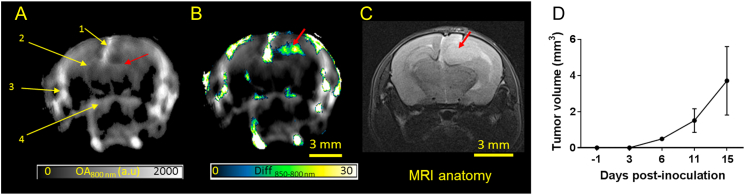
Figure 1.
Anatomical imaging of orthotopic glioblastoma in mice using MSOT. (A) In vivo single wavelength (800 nm) optoacoustic image depicting the anatomy of an intact mouse brain with U87MG glioblastoma. The slice is at bregma +2 mm. Brain structures such as superior sagittal sinus (SSS, 1), middle cerebral artery (MCA, 2), superficial temporal arteries (TA, 3) and posterior communicating artery (PCA, 4) and altered symmetry at the right MCA (red arrow) are visible. (B) Difference of the optoacoustic images acquired at 850 and 800 nm, highlighting the tumor location and shape (red arrow). (C) T2 weighted MRI anatomy image of the corresponding brain slice with the hyperintense lesion (red arrow) representing the tumor. (D) Graph showing increase in tumor volume across different days post tumor inoculation calculated using the difference in OA signals at 850 and 800 nm (n = 3).