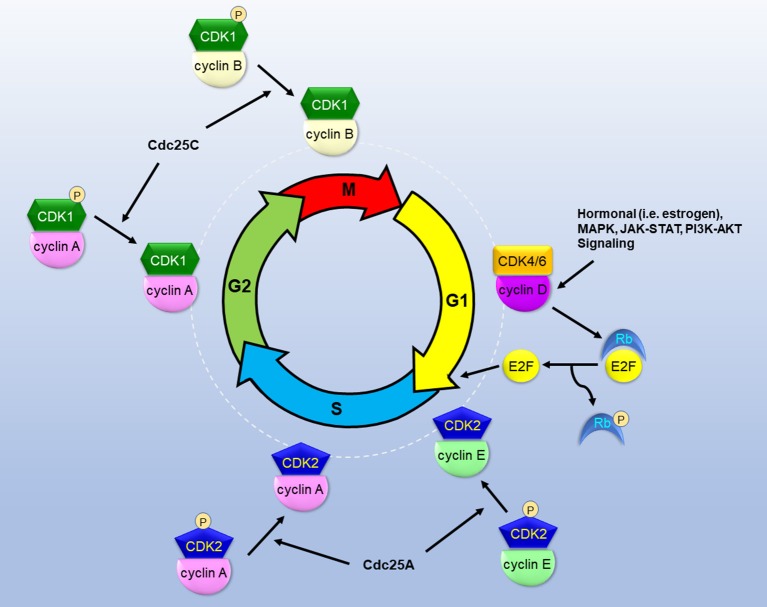
Figure 1.
The roles of CDKs in the cascade of cell cycle. CDKs bind to specialized cyclins to form active complexes that drive cell cycle phase progression and transition into next phases. Growth and mitogenic signals induce cyclin D and activate CDK4, thereby inactivating Rb and releasing E2F to instigate G1 phase progression. Cdc25 phosphatases dephosphorylate and activate CDKs to promote S/G2/M phase progression.