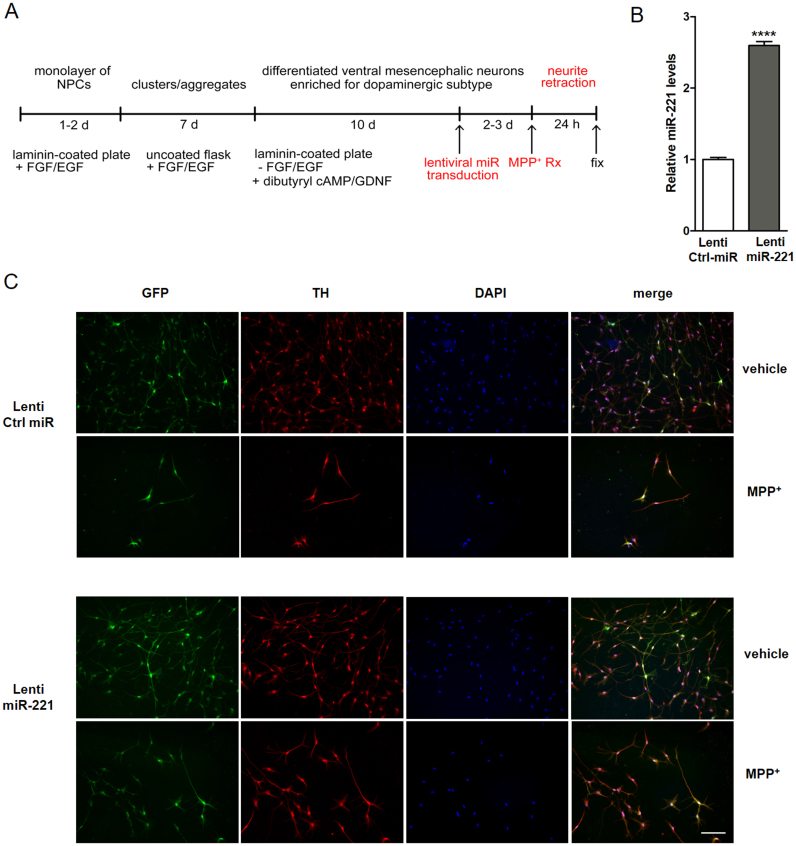
Fig. 4.
miR-221 mitigates the loss of neuron morphology in terminally differentiated, human ReNcell VM dopaminergic neurons treated with MPP+. To investigate the role of miR-221 in terminally differentiated human neuronal cells, (A) neural progenitor cells (NPCs) derived from the ventral mesencephalon (ReNcell VM) were terminally differentiated to dopaminergic neurons using an established pre-aggregation protocol. (B) Differentiated ReNcell VM cells were transduced with lentivirus containing control (lenti-Ctrl miR) or miR-221 (lenti-miR-221). Cells transduced with lenti-miR-221 showed robust up-regulation of mature miR-221. (C) These cells were treated with 0.5 mM MPP+ or vehicle (DMEM) for 24 h. Differentiated ReNcell VM cells exhibited GFP expression from viral transduction, stained positively for the dopaminergic neuron marker tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). Following MPP+ exposure, cells exhibited loss of neurite morphology, which was mitigated by miR-221 over-expression (Scale bar: 100 µm). Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences (****p ≤ 0.0001) relative to control. (B) analyzed using two-tailed student's t-test.