Figure 2. STING (R284S) Constitutively Localizes to the Peri-nuclear Area.
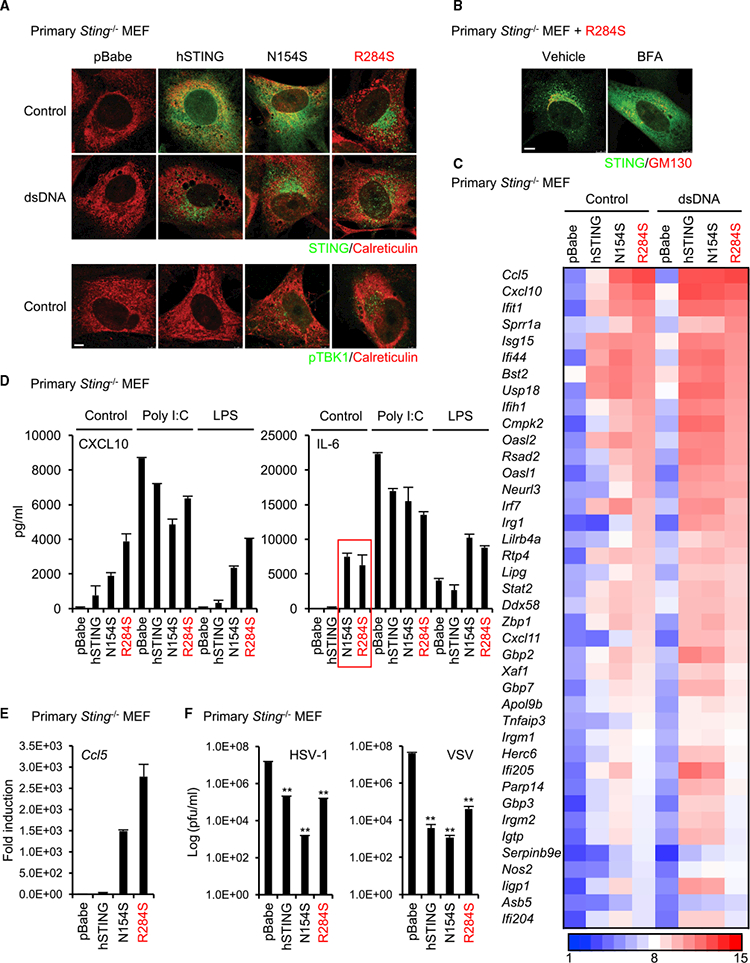
(A) Primary Sting-’- MEF cells were reconstituted with wild-type STING or its mutants (N154S and R284S) using a retrovirus. The reconstituted cells were treated with dsDNA(4 mg’mL) using Lipofectamine 2000 for 9 hr. After fixation, the cells were stained with the indicated antibodies, and then the localization of STING and phosphorylated TBK1 (pTBK1) was observed using a confocal microscope. Calreticulin is an ER marker. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(B) The reconstituted cells with R284S were treated with BFA (5 μg’mL) for 9 hr. The localization of STING was observed as described in (A). GM130 is a c/s-Golgi marker. Scale bar, 7.5 μm.
(C) Total RNA was purified from the reconstituted cells after treatment with dsDNA as described in (A) and then examined for gene expression using the Affymetrix GeneChip array. The scale represents the intensity of gene expression (log2 scale).
(D) The amounts of CXCL10 or IL-6 in the supernatants of the reconstituted cells were measured by ELISA after treatment with poly(I:C) (1 mg’mL) using Lipofectamine 2000 or LPS (10 mg/mL) for 15 hr.
(E) cDNA was synthesized from total RNA that was extracted from the reconstituted cells, and then real-time PCR was performed with the Ccl5 probe.
(F) The reconstituted cells were infected with HSV-1 or VSV at MOI = 1 for 24 hr, and then a plaque assay was performed to determine the viral titers. Data shown here are the averages ± SD (n = 3). **p < 0.01, determined by Student’s t test. See also Figure S2.
