Figure 4. AMPK Inhibitors Are Potential Therapeutic Drugs for STING-Induced Inflammatory Diseases.
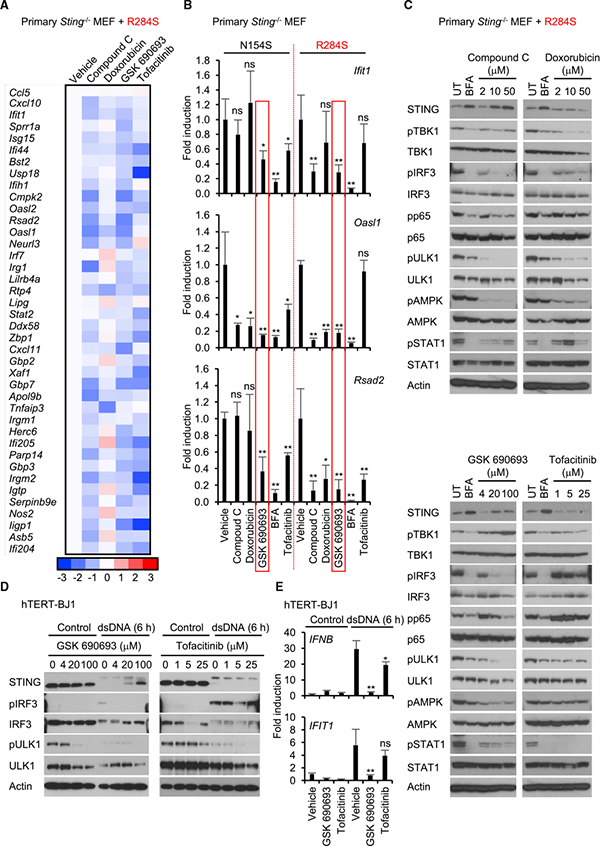
(A) The reconstituted Sting−/−MEF cells expressing R284S were treated with the indicated drugs (compound C, 10 μM; doxorubicin, 10 mM; GSK 690693,20 μM tofacitinib, 5 mM)) for 9 hr. Total RNA was purified and then examined for gene expression compared with vehicle as described in Figure 2C. The scale represents the intensity of gene expression (log2 scale).
(B) The reconstituted cells expressing N154S or R284S were treated with the indicated drugs as described in Figure 4A. Realtime PCR was performed with Ifit1, Oasl1, or Rsad2 probe.
(C) The reconstituted cells expressing R284S were treated with the drugs at the indicated concentration for 9 hr. Wester blots were performed for the cell lysates with the indicated antibodies. pULK1 and pAMPK indicate phosphorylated serine 555 on ULK1 (S555) and threonine 172 on AMPKα (T172), respectively. UT,untreated.
(D) hTERT-BJ1 cells were pre-incubated with the drugs at the indicated concentration for 1 hr. Then the cells were treated with dsDNA for 6 hr as described in Figure 2A. Western blots were performed for the cell lysates with the indicated antibodies.
(E) hTERT-BJ1 cells were pre-incubated with drugs (GSK 690693,20 μM; tofacitinib, 5 μM))for 1 hr. Then the cells were treated with dsDNA for 6 hr as described in Figure 2A. Real-time PCR was performed with the IFNB1 or IFIT1 probe. Data shown here are the averages ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, determined by Student’s t test. See also Figure S4.
