Figure 1.
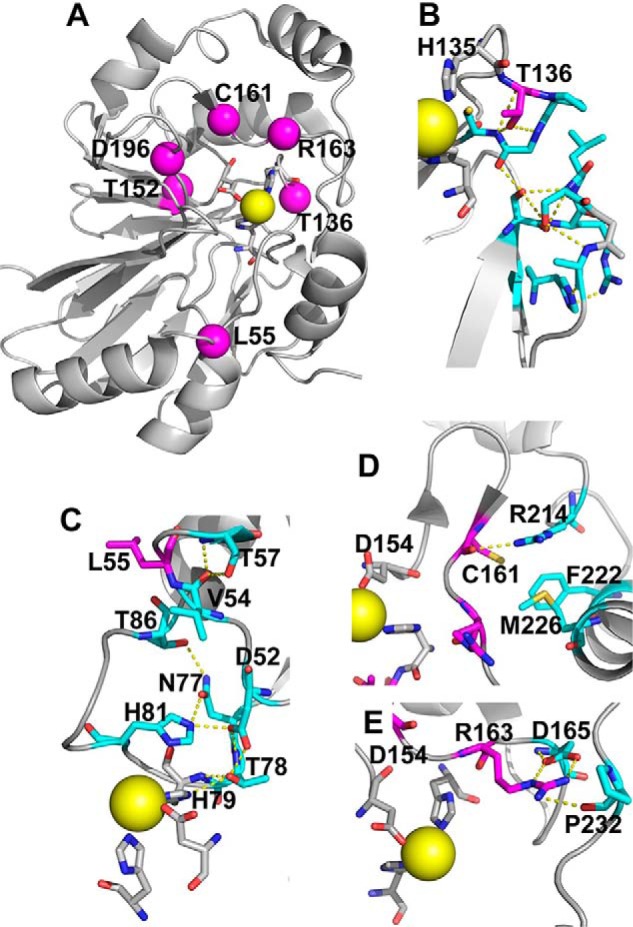
Structural analysis of PDO mutations. The structure of human PDO (Protein Data Bank entry 4CHL) was used to map the locations of PDO mutations characterized in this study. A, iron (yellow sphere) ligands (His-79, His-135, and Asp-154) that form the 2-His-1-Asp facial triad are shown in stick representation. Locations of the six residues mutated in patients that were characterized previously and/or herein, Leu-55, Thr-136, Thr-152, Cys-161, Arg-163, and Asp-196, are shown by magenta spheres. B, close-up showing the side-chain interactions of Thr-136, which would be lost in the T136A mutation. C, close-up of Leu-55 displays interactions that would potentially be lost due to the L55P mutation. D, close-up of the interaction involving Cys-161, which would be perturbed in the C161Y mutant. E, close-up of Arg-163 highlights the interactions that might be lost in the R163W mutant.
