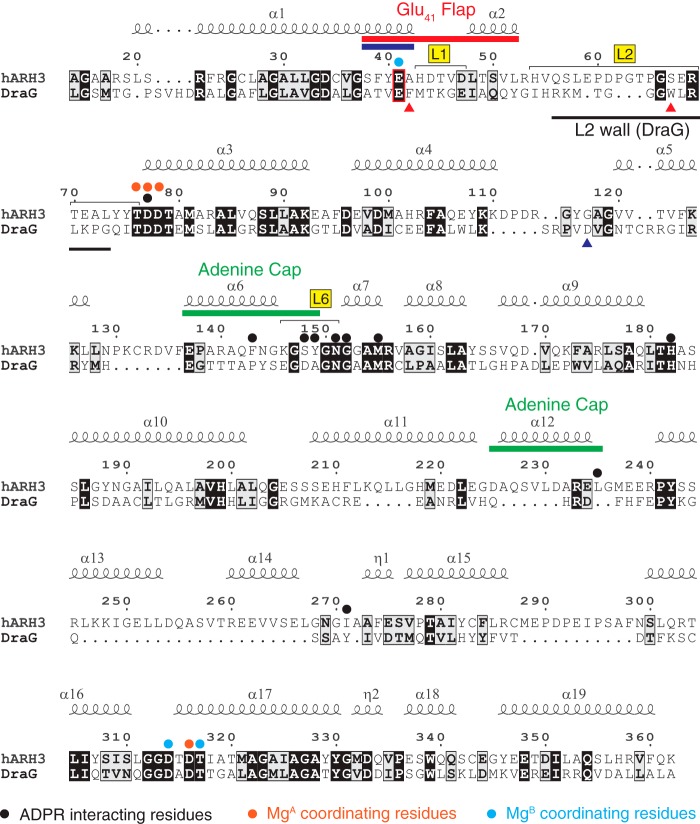
Figure 2.
Structure-based alignment of ARH3 and DraG with structural elements and residues that are important for function. The Glu41 residue of the Glu41-flap of ARH3 that undergoes a large conformational change upon ADPR binding is indicated by a red box. A part of L2 of DraG (L2 wall) completely blocks the conformational change of α1 and restricts its activity to cleavage of mono(ADP-ribosyl)ated substrates. The end of α1 in ARH3, which exists as 310-helix in the unliganded form and undergoes 310-to-α transition upon ADPR binding (Fig. 4a), is indicated by a blue bar. Two aromatic residues in DraG that stabilize the L2 wall are indicated by a red triangle. Asp97 in DraG that is essential for the cleavage of MARylated arginine is indicated by a blue triangle.