Figure 2.
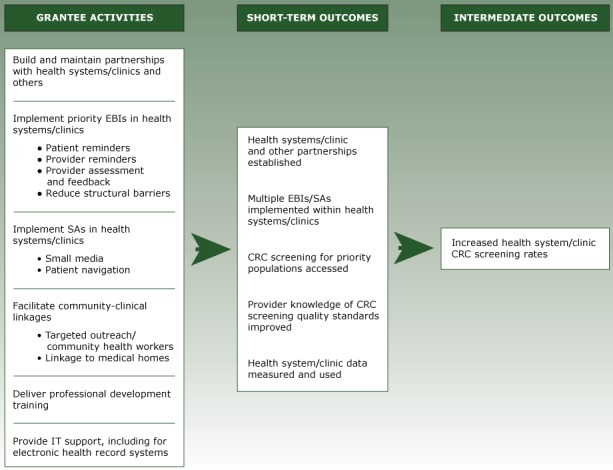
Program Logic Model Showing Activities and Outcomes of the Colorectal Cancer Control Program, Program Year 1, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, July 2015 through June 2016. Abbreviations: CRC, colorectal cancer; EBIs, evidence-based interventions; SAs, supporting activities.
