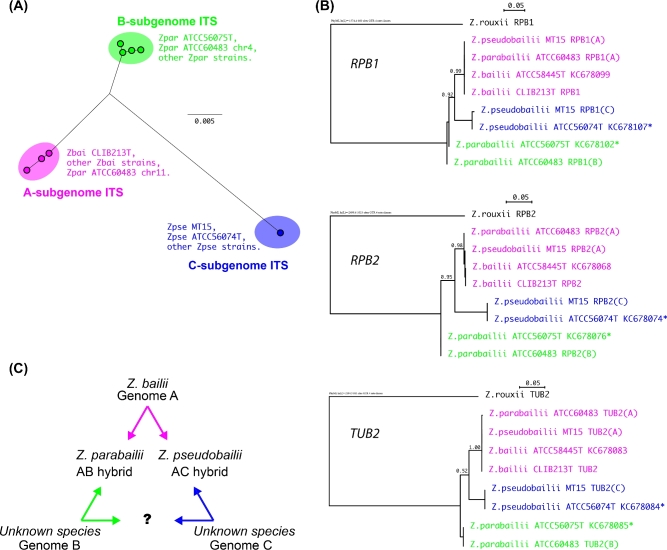
Figure 1.
MT15 is a strain of Z. pseudobailii. (A) Unrooted phylogenetic tree of the ITS region of ribosomal DNA. The sequences analyzed were ITSs of multiple strains of Z. pseudobailii (Zpse), Z. parabailii (Zpar) and Z. bailii (Zbai), including the type strains of each species, from Suh et al. (2013), as well as ITS sequences identified in the genome assemblies of MT15 (one locus) and Z. parabailii ATCC60483 (two loci, on chromosomes 4 and 11; Ortiz-Merino et al.2017). Nodes represent individual ITS sequence variants; many strains have identical sequences. The scale bar indicates numbers of nucleotide substitutions per site. (B) Phylogenetic trees for RPB1, RPB2 and TUB2 genes. The A, B and C subgenomes are color coded as in panel A. Asterisks beside NCBI sequence accession numbers indicate type strain sequences that originally contained ambiguous sites (Suh et al.2013), for which we inferred the B- or C-copy sequence by subtracting the A-copy sequence. The scale bars indicate numbers of nucleotide substitutions per site. (C) Triangular relationship among the genomes and species in the Z. bailii species complex.