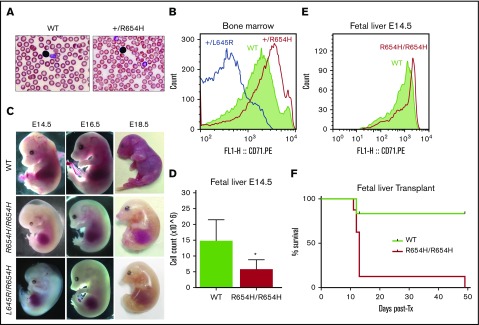
Figure 2.
Phenotype of the RBC21 mouse. (A) Peripheral blood smears of 7-week-old WT and RBC21 heterozygous (Tfrc+/R654H) mice (original magnification ×400; hematoxylin and eosin stain). Heterozygotes show microcytic red cells with mild pallor. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of CD71 expression levels, performed on live Ter-119+ bone marrow erythroblasts of WT, RBC6 (Tfrc+L645R), and RBC21 (Tfrc+/R654H) mice. (C) Timed pregnancies showing WT, RBC21 homozygous (TfrcR654H/R654H), and RBC6/RB21 double-heterozygous (TfrcL645R/R654H) embryos, dissected at embryonic days 14.5, 16.5, and 18.5. (D) Fetal liver live cell counts performed on WT and RBC21 homozygous (TfrcR654H/R654H) embryos at embryonic day 14.5 (n = 4). (E) Flow cytometric analysis of CD71 expression levels, performed on live Ter-119+ fetal liver cells of WT and RBC21 homozygous (TfrcR654H/R654H) embryos at embryonic day 14.5. (F) Survival curve of irradiated adult mice transplanted with WT or RBC21 homozygous (TfrcR654H/R654H) fetal liver cells, extracted from E14.5 embryos. Median survival of homozygous cohort, 13 days (n = 12). *P < .05. Tx, treatment.