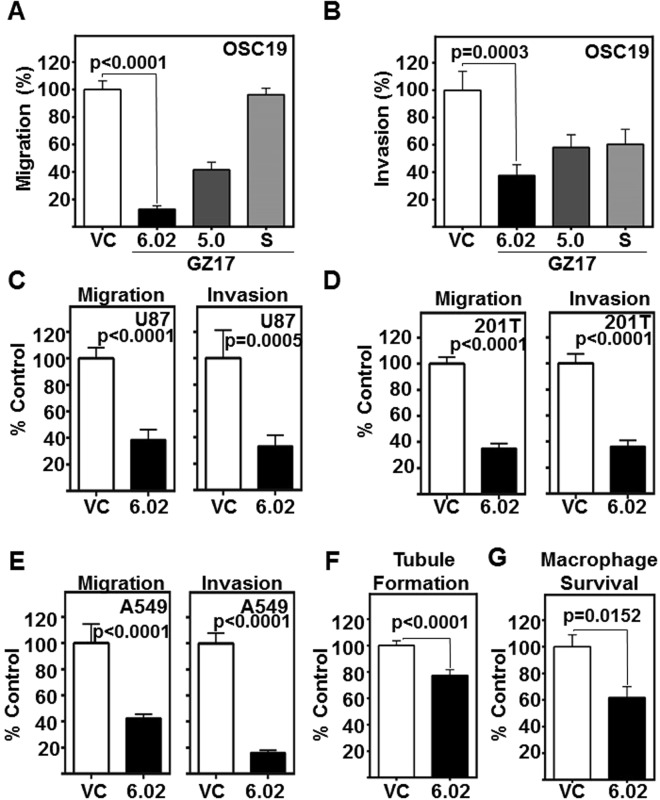
Figure 2.
GZ17 formulations mitigate HNSCC invasion and migration, and angiogenesis. (A,B) HNSCC cells (OSC19; 2 × 103 cells/ well, plated in triplicate) were treated with vehicle control or ED50 concentrations of GZ17-6.02, -05.00 or -S. Cell migration and invasion was assessed at 24 h. The number of cells that (A) migrated or (B) invaded were counted and normalized to the cell viability. Percent migration or invasion relative to the vehicle control is depicted in the graphs. Cumulative data represents three individual experimental repeats and error bars represent ± SEM. (C,D,E) Glioblastoma (U87), and (D and E) lung cancer (201T and A549) were assessed for GZ17-6.02 inhibition of migration and invasion. Cumulative data represents three individual experimental repeats and error bars represent ± SEM. (F) GZ17-6.02 attenuates the angiogenic potential of HUVEC in vitro. HUVEC cells were treated with the ED50 dose (derived from OSC19) of GZ17-6.02 and imaged 6 h after treatment and tubule formation was assessed. Total tube length analyzed using Pipeline software from 15 random fields from each repeat, and normalized to vehicle control treated cells (VC). Cumulative data represents three individual experimental repeats and error bars represent ± SEM. (G) GZ17-6.02 inhibits tumor-promoting macrophage survival. Macrophage cell line Thp1 were treated with 60 µg/ml GZ17-6.02 for 48 h. Viable cells were counted using trypan blue dye exclusion. Graph represents cumulative results from five independent experiments and error bars represent ± SEM.