Fig. 5.
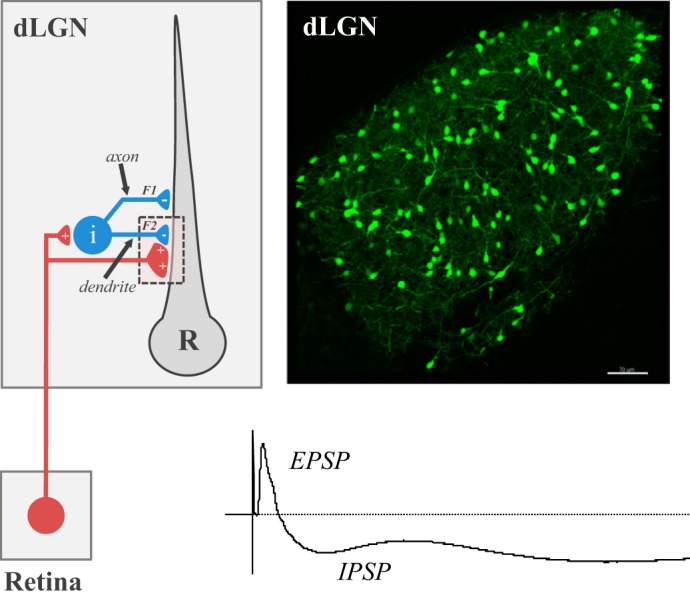
Feed-forward inhibition in dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN). Left: circuit diagram showing the pattern of synaptic connectivity between a retinal axon, intrinsic interneuron (i), and relay (R) neuron in dLGN. Retinal (red) synapses make glutamatergic excitatory connections onto an interneuron and relay neuron. Interneurons form GABAergic inhibitory connections with relay neurons through axodendritic (F1) and dendrodendritic (F2) synapses. Right: coronal section through dLGN of a GAD-67 green fluorescent protein (GFP) mouse where GFP is expressed in intrinsic interneurons. Scale bar: 100 μm. Bottom: voltage response from a relay neuron showing the excitatory (EPSP) and inhibitory (IPSP) postsynaptic activity evoked by electrical stimulation of the optic tract.
