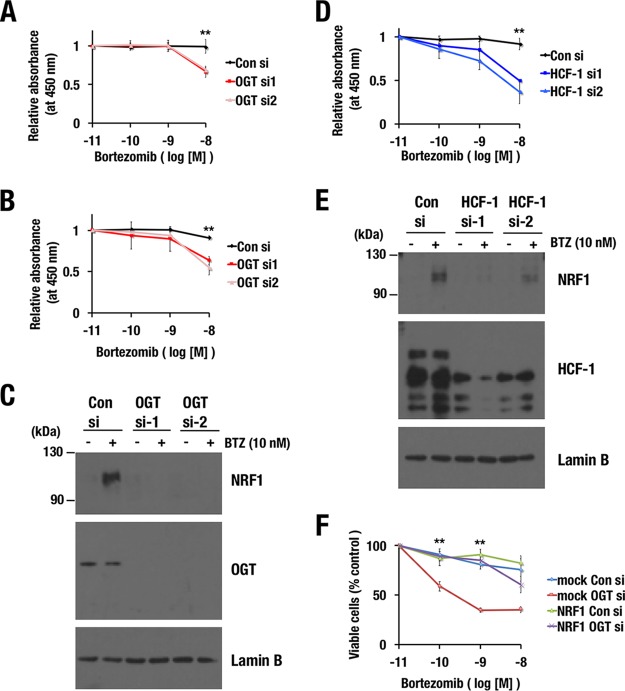
FIG 10.
Inhibition of the OGT/HCF-1 complex sensitizes cancer cell lines to a proteasome inhibitor. (A, B, and D) Effects of OGT (A and B) or HCF-1 (D) knockdown on the viability of MDA-MB-231 (A and D) and NCI-H460 (B) cells in the presence of bortezomib. At 24 h after the transfection of control siRNA or OGT or HCF-1 siRNAs, the cells were reseeded in 96-well plates. The next day, the cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of bortezomib for 24 h. Cell viability was monitored using Cell Counting Kit-8. Averages and SD were calculated from quadruplicate samples. Relative absorbances of samples that were treated with 10−11 M bortezomib were set to 1. **, P < 0.01. (C and E) Endogenous NRF1 accumulation in response to bortezomib treatment in MDA-MB-231 cells. MDA-MB-231 cells that were transfected with control siRNA, OGT siRNAs (C), or HCF-1 siRNAs (E) were treated with 10 nM bortezomib at 72 h after the transfection. After 4 h, nuclear extracts were prepared. Lamin B was used as a loading control. (F) Effects of NRF1 overexpression on OGT knockdown-induced sensitization to bortezomib. 293F cells expressing NRF1-3×FLAG or containing an empty vector (mock) were transfected with control siRNA or OGT siRNAs. At 24 h after the transfection, the cells were reseeded in 96-well plates. The next day, the cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of bortezomib for 48 h. Cell viability was assessed using a trypan blue exclusion test. Averages and SDs were calculated from the results of three independent experiments. Viable cell numbers for samples that were treated with 10−11 M bortezomib were set to 100%. **, P < 0.01.