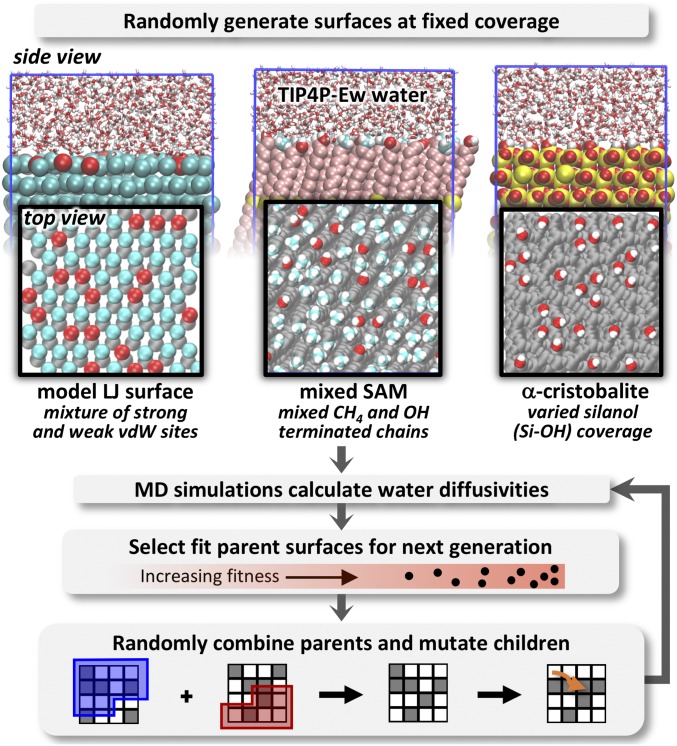
Fig. 1.
A schematic of the workflow for the genetic algorithm to optimize (minimize or maximize) hydration water dynamics via repatterning of surfaces at various fixed coverages of hydrophilic groups. Surfaces studied include the face of -cristobalite with varied silanol coverage, SAM surfaces with mixed methyl- and hydroxyl-terminated chains, and idealized surfaces of mixed binary LJ particles with either strong or weak LJ−water van der Waals (vdW) interactions.