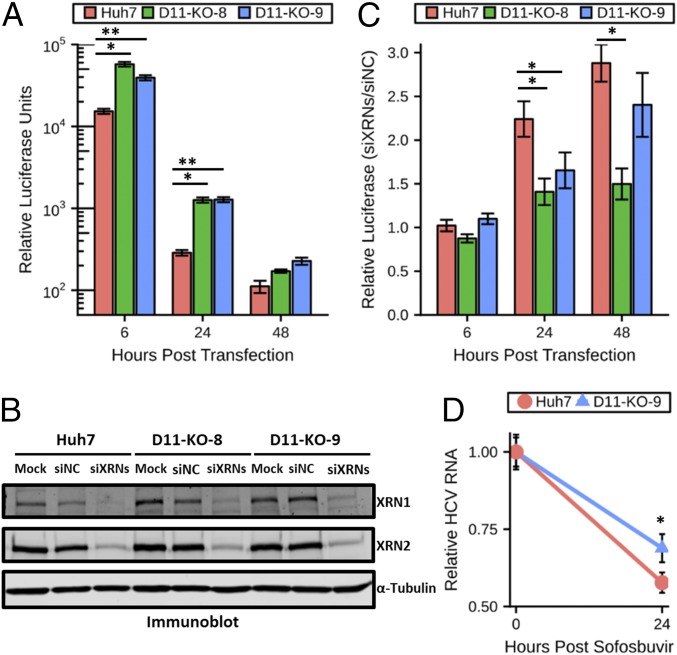
Fig. 2.
HCV restriction activity of XRNs is reduced in cells lacking DUSP11. (A) sgJFH1-Rluc-GND (nonreplicative polymerase mutant) replicon luciferase assay in parental Huh7 cells and two independent DUSP11 knockout clones (D11-KO-8 and D11-KO-9). Luciferase assays were performed at the indicated times post replicon RNA transfection. The mean ± SEM of three individual experiments is presented. (B) Confirmation of siRNA knockdown of XRN1 and XRN2 in parental Huh7 cells and two independent DUSP11 knockout clones (D11-KO-8 and D11-KO-9) by immunoblot. Huh7 were either mock transfected (Mock) or transfected with either an irrelevant control siRNA or a pool of XRN1- and XRN2-specific siRNAs (siXRNs). Cell lysates were harvested 48 h post transfection and assayed by immunoblot with the indicated antibodies. (C) sgJFH1-Rluc replicon luciferase assay in parental Huh7 cells and two independent DUSP11 knockout clones (D11-KO-8 and D11-KO-9) treated with siNC or a pool of siXRNs. Luciferase assays were performed at the indicated times post replicon RNA transfection. The mean ± SEM of three experiments is presented. (D) Huh7 and D11-KO-9 cells were infected with HCV for 96 h and treated with 5 μM sofosbuvir, and HCV RNA levels were quantified at the indicated times post treatment. The mean ± SEM of eight samples is presented. Statistical significance was assessed by Student’s t test and is indicated as follows: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.