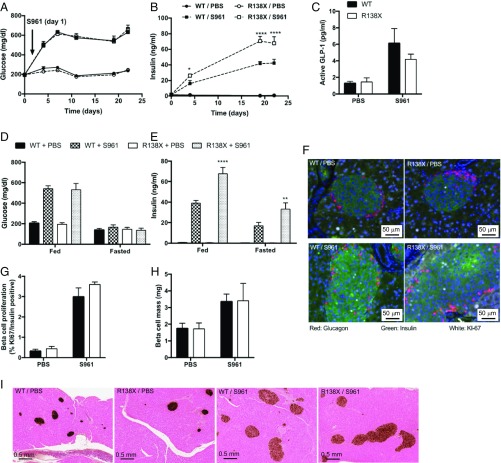
Fig. 3.
R138X mice secrete more insulin under chronic hyperglycemia caused by the insulin receptor antagonist S961. (A) Nonfasted plasma glucose levels in R138X and WT mice continuously treated with the insulin receptor antagonist S961 (20 nmol/wk) or PBS for 22 d. (B) Nonfasted plasma insulin on day 0, 4, 19, and 22 R138X and WT mice treated with S961 (20 nmol/wk) or PBS. (C) Plasma active GLP-1 levels in WT and R138X mice after 22 d of treatment. (D and E) Fed and fasted glucose (D) and insulin (E) levels measured day 19 and 20 after initiation of treatment. (F) Immunohistochemistry for Ki-67 (white), insulin (green), and glucagon (red). (G) Quantification of Ki-67 and insulin double-positive cells. (H) Quantification of pancreatic insulin staining shown in I. (I) Histology for insulin in pancreas isolated from WT and R138X mice after 22 d of treatment. Values represent the means ± SEM (n = 5 to 7 mice per treatment and genotype). *P < 0.5, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.